Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
W
M
(a)
Magnet
(b)
Magnet
T
M
W
C
T
C
L
C
a
G
Aluminum plate
Aluminum plate
Fig. 3.
Structural parameters of meander-line coil EMATs. (a) is the 3-D view and (b)
is the X-direction view.
A meander-line coil EMAT with a certain parameter combination is taken as
an example to illustrate the modeling process. First, 3-D physical whole model
and DMF model of the meander-line coil EMAT are established. Tetrahedron
elements are adopted to divide the physical models into finite element models.
The region under the magnet is further subdivided. The refinement significantly
improves the calculation accuracy, whereas the calculation time increases greatly.
In practice, when the calculation results hardly vary with subdivision, further
refinement is unnecessary.
The Lorentz force density distribution can be calculated. To make sure the
obtained Lorentz forces approximate to point forces, the force action region
should be subdivided into tiny hexahedron elements. Simulation results show
that Lorentz forces mainly concentrated with an area about 1.5 times of the
coil's outline on the plate surface within the skin depth. Beyond this region,
Lorentz forces are less than 1% of that in the region. So this region is exported
to point forces by a 3-D grid.
To clearly describe the Rayleigh waves, the aluminum plate surface is also
divided into many square elements. After dividing Lorentz forces into point
forces, Rayleigh wave displacements at each element on the aluminum plate
surface can be calculated, and displacements at other points can be acquired by
interpolation method.
4 Simulation and Analysis
In these models, tone-burst current signals with different amplitudes are sent into
meander-line coils. The energy of Rayleigh waves is proportional to the square
of their vibration amplitudes, and the divergence angle is defined as sound beam
at -3dB value below the peak response, which is related to the detection area.
The detectability of Rayleigh wave EMATs depends on the vibration amplitude
and the divergence angle. In this paper, these two parameters are chosen as main
targets to study Rayleigh wave distributions.
Fig. 4 illustrates the Rayleigh wave sound distribution on aluminum plate
generated by meander-line coil EMATs, which shows that Rayleigh waves have
good directivity. The Rayleigh wave vibration amplitude and divergence angle
can be obtained through the sound field distribution.













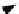














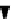




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search