Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
framework of the algebraic identification theory, which utilizes the differential al-
gebraic and operator calculus as main mathematical tools. Section 4 gives the key
parameters identification scheme for second-order highway trac model based
on differential algebraic methodology. In section 5, a number of simulations are
conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed the algebraic identification
scheme. Finally, the main conclusions are summarized and a few open problems
are discussed in section 6.
2 Dynamic Model of Highway Stretch
Macroscopic trac flow model are employed to describe the dynamic behavior of
trac flow of a highway stretch using aggregate variables, including space-mean
speed, density (or occupancy), and flow rate. The second-order macroscopic traf-
fic flow model METANET is employed in this paper. It is also the foundation
of a large number of trac control studies, due to the ability to realistically
reproduce trac phenomena [16].
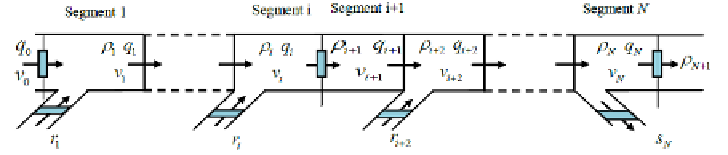
Fig. 1.
Highway section divided into
N
sections
METANET model is discrete both in time and space. To be specific, one high-
way stretch is subdivided into segments of equal length (usually about 500m),
as is shown in figure 1. The METANET models are as follows:
T
Δ
i
λ
i
[
q
i−
1
(
k
)
ρ
i
(
k
+1)=
ρ
i
(
k
)+
−
q
i
(
k
)+
r
i
(
k
)
−
s
i
(
k
)]
(1)
s
i
(
k
)=
β
i
(
k
)
·
q
i−
1
(
k
)
(2)
v
i
(
k
+1)=
v
i
(
k
)+
T
+
T
τ
[
V
(
ρ
i
(
k
))
−
v
i
(
k
)]
Δ
i
v
i
(
k
)[
v
i−
1
(
k
)
−
v
i
(
k
)]
relaxation term
convection term
(3)
vT
τΔ
i
[
ρ
i
+1
(
k
)
ρ
i
(
k
)]
ρ
i
(
k
)+
κ
−
r
i
(
k
)
v
i
(
k
)
ρ
i
(
k
)+
κ
ramp influence term
δT
Δ
i
λ
i
−
−
anticipation term
1
α
(
ρ
ρ
cr
)
α
]
V
(
ρ
)=
v
f
exp[
−
(4)

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search