Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
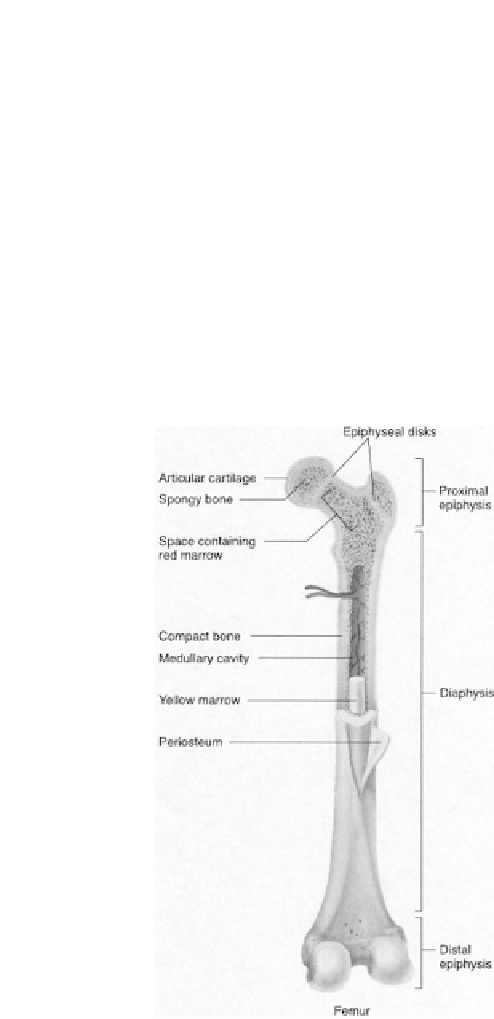
which is less dense and less stiff than compact bone. usually bone is
composed of a relatively dense outer layer of cortical bone covering
an internal mesh-like structure (average porosity of 75-95%) of
cancellous bone, the density of which is about 0.2 g/cm
3
but it may
vary at different points (Fig. 1.10). Cortical bone makes up a large
portion of the skeletal mass; but due to its high density (~1.80 g/cm
3
)
it has a low surface area. Cancellous bone has an open meshwork or
honeycomb-like structure. It has a relatively high surface area but
forms a smaller portion of the skeleton. Bone is a porous material
with the pore sizes range from 1 to 100 μm in normal cortical bones
and 200-400 μm in trabecular bones. About 55-70% of the pores
in trabecular bones are interconnected. The porosity reduces the
strength of bones but also reduces their weight [27, 83, 84, 105-107,
454, 544, 552-556, 569-573].
Figure 1.10
General structure of a mammalian bone. Other very good
graphical sketches of the mammalian bone structure are
available in Refs. [87, 537].

Search WWH ::

Custom Search