Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
hydrophilic aldehyde group (head) (Kubo
et al.
, 1995a, 2003a). It is well known that the
hydrophobicity of molecules is often associ-
ated with biological action (Hansch and
Dunn, 1972). However, the rationale for this
observation, especially the role of the hydro-
phobic portion itself, is still poorly under-
stood and widely debated. Aliphatic
2
E
-alkenals represent an excellent model for
investigating structure and activity relation-
ships (SARs) related to this problem because
these molecules possess the same hydrophilic
portion (the enal group) but different hydro-
phobic alkyl portions. Thus, in addition to
their potential as anti-
Salmonella
agents, an
evaluation of these 2
E
-alkenals against
Salmonella
may provide new insights into
the molecular basis of their antibacterial
action. Aliphatic 2
E
-alkenals and their related
analogues are common in many plants (Kubo
and Kubo, 1995; Kubo
et al.
, 1996, 1999;
Kubo and Fujita, 2001) and readily available.
We tested a homologous series of aliphatic
2
E
-alkenals and their corresponding alkanals
from C5 to C13, as well as a series of alkanols
and other related compounds, for antibacte-
rial activity against
S. choleraesuis
subsp.
choleraesuis
ATCC 35640, one of the most
frequent sources of bacterial food infections
(Frazier and Westhoff, 1988).
16.2
2
E
-Alkenals
In previous reports, 2
E
-hexenal (C6) (
1
) (see
Fig. 16.1 for structures) was described to
show a broad antimicrobial spectrum (Kubo
and Kubo, 1995; Kubo
et al.
, 1995a;
Bisignano
et al.
, 2001; Gardini
et al.
, 2001;
Lanciotti
et al.
, 2003), which includes activ-
ity against
S. choleraesuis, Escherichia coli,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter
aerogenes, Proteus vulgaris
(Kubo and
Fujita, 2001) and
S. choleraesuis
, as well as
Helicobacter pylori
(Kubo
et al.
, 1999). This
aliphatic a,b-unsaturated aldehyde is
known as 'leaf aldehyde' (Hatanaka, 1993)
H
H
O
O
1
4
H
H
O
O
6
3
H
H
O
O
2
7
H
HO
O
8
5
H
HO
16
O
HO
19
11
O
HO
HO
12
9
O
HO
13
HO
10
HO
14
O
HO
O
18
17
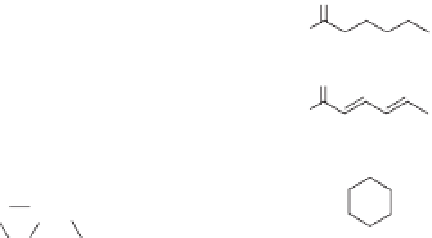
Fig. 16.1.
2
E
-Alkenals, alkanals, alkanols and related compounds.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search