Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
OH
6
5
HO
H
OH
H
H
4
(CH
2
)
14
1
HO
HO
OH
H
3
2
OH
(CH
2
)
7
(CH
2
)
5
HO
OH
OH
grebustol B
(leaves of
Grevillea robusta
)
bisnorstriatol
(stems of
Grevillea floribunda
)
CH
3
O
OH
H
3
C
HO
(CH
2
)
3
(CH
2
)
3
OH
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
COO
OCOCH
3
(CH
2
)
n
CH
3
1: n = 16 cichoriol A
oncostemonol A
2: n = 18 cichoriol B
3: n = 19 cichoriol C
4: n = 20 cichoriol D
(aerial parts of
Cichorium spinosum
)
H
HO
O
OH
O
OH
OH
OH
HO
grevilloside A
(leaves of
Grevillea robusta
)
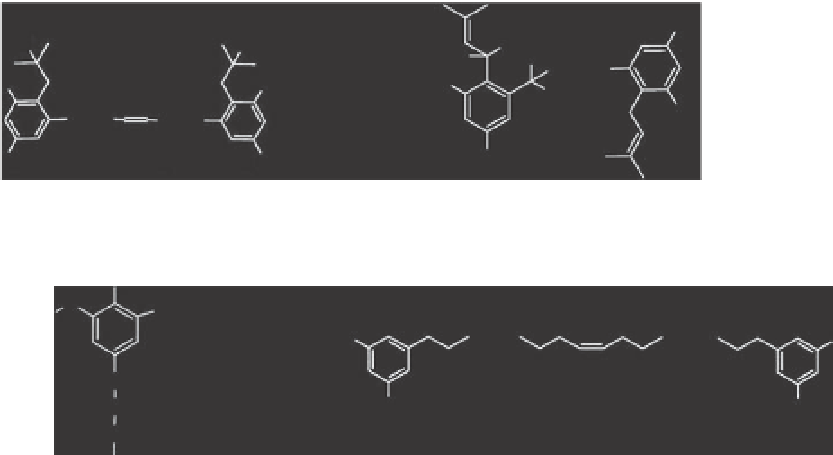
Fig. 10.3.
Alkylresorcinol derivatives isolated from plant sources.
l,3-dihydroxy-2-alkyl and l,3-dihydroxy-2,5-
dialkylbenzenes (Barrero
et al
., 1994); grevil-
losides isolated from leaves of
Grevillea
robusta
, which are 5-n-ARs O-glucosylated
at position 1 of the benzene ring (Yamashita
et al
., 2008); and the 5-n-AR glycosides of
arabinose found in root exudates of rice
seedlings (Kong
et al
., 2002).
The Anacardiaceae and Gramineae are
important sources of ARs. In Anacardiaceae,
the cashew tree (
Anacardium occidentale
),
originating from Brazil, is the major and the
cheapest source of meta alkylphenols avail-
able in Latin America (De Lima
et al
., 2008).
The fruit of the tree consists of an outer
shell (epicarp), a tight-fitting inner shell
(endocarp), and a strongly vesicant cashew
nut-shell liquid (CNSL, Fig. 10.4a) con-
tained between the inner and outer shell
(pericarp). This oily liquid is extracted by
roasting cashew nuts. On the basis of the
mode of extraction, CNSL is classified into
Search WWH ::

Custom Search