Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
the coordinate covalent bonds between the triterpene framework and carbohydrate
residues attached at carbons 3 and 24 renders all the mogrosides inert to thermal
and enzymatic degradation (Heimbach 2009).
Metabolism
The mogroside content of LHG extracts is thought to be undigested by humans
and, therefore, zero calorie. On the basis of unpublished reports cited in the GRAS
notifi cation (Heimbach 2009), LHG extract has no effect on blood glucose, is
non-insulinogenic and not metabolised by colonic fl ora. The basis of the extract's
GRAS status is predominantly evidence of substantial long-term historical use
and by a number of animal studies showing lack of toxicity. The GRAS notice
gives details of the latter.
There are indications of pharmacological activity in the extracts, for example,
in ameliorating diabetes in mice (Song
et al.
2006, 2007), but it is not clear if the
effects were caused by mogrosides or other co-extracted plant constituents.
Sensory properties
LHG has a more delayed sweetness onset than rebaudioside A and a predominantly
sweet linger. There is a liquorice note in the profi le that is more obvious at higher
concentrations, as well as minor traces of bitterness.
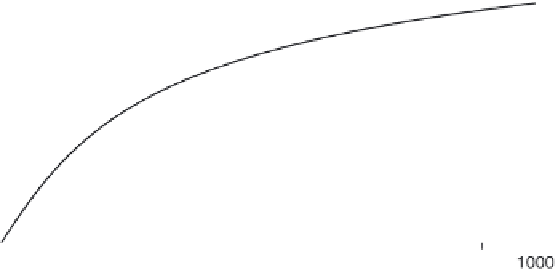
The concentration-response curve for a 40-50% mogroside V product is
shown in Fig. 3.7. The potency is 120 at 5% SE. This is consistent with the value
of 256 at 5% SE quoted for pure mogroside V (Kinghorn and Compadre 1991).
Much higher potencies are often quoted in the literature, for example, 425 at 5%
Fig. 3.7
Concentration-response curve for a lo han guo extract in water. Mogroside V
content about 45% and about 75% total mogrosides.



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search