Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Stevioside, rebaudioside A (Fig. 16.11) and other glycosides of steviol, an
ent-
kaurene diterpenoid, derived from the leaves of the South American plant
Stevia rebaudiana
Bertoni (Kinghorn
et al.
2010), are intensely sweet (200-300
times sweeter than sucrose). These glycosides are permitted food sweeteners in
many Asian countries. They have similar potency to synthetics like aspartame, but
are more stable in beverages (Prakash
et al.
2008) and have superior photostability
over certain artifi cial sweeteners (Clos
et al.
2008). Nevertheless, they are prone
to hydrolysis over a period of months (Wölwer-Riecker
et al.
2010).
Rebaudioside A has been granted GRAS (Generally Recognised As Safe)
status in the US and no health hazards have been reported, although there was
some concern over the safety of hydrolysis products (including steviol). In Europe,
steviol glycosides (rebaudioside A) were authorised in 2011 on the basis of a
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) report (EFSA, 2010).
Emulsion liqueurs, particularly those based on dairy cream, are some of the
most popular of all liqueurs. Their appeal, apart from fl avour and taste, depends on
the smooth appearance and mouthfeel resulting from persistent homogeneity. A
cream liqueur is basically an emulsion made from cream, sweetened ethanol/water,
possible fl avourings, possible colourants, caseinate emulsifi er, a stabiliser and a
monoglyceride ester surfactant (Fig. 16.12). The stabiliser is typically a calcium
or trisodium citrate sequestering agent, since a high ionic content leads to
unstable emulsions. The ingredients are typically mixed and then homogenised
in a radial diffuser homogeniser at 45-55°C and 20-30 MPa pressure, although
recently the use of a high-pressure homogeniser operating at 20-250 MPa
produced a liqueur with improved shelf life with regard to separation (Heffernan
et al.
2009).
Dairy cream liqueurs, made as above, are generally stable emulsions if the pH
is above ca. 6.4, if the ethanol content is below ca. 20% ABV (typically ca. 17%
ABV) and if stored at temperatures well below 25°C. Use of whey protein extract
in place of cream has been found to increase emulsion stability (Kaustinen and
Fig. 16.11
Stevioside and Rebaudioside A structures.






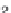


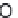












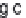























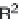





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search