Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
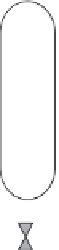
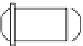
Fig. 12.4
Typical components of subcritical water extraction equipment.
either hydro-distillation or subcritical water at 150°C/5 MPa. These authors
demonstrated that a higher yield can be obtained and the extraction can be carried
out in 15 minutes using subcritical water compared to three hours for hydro-
distillation. In both cases the levels of oxygenated compounds were higher in the
extracts prepared using subcritical water.
Unlike supercritical carbon dioxide extraction, there are so far no commercial
plants that are using subcritical water to extract fl avour ingredients. This is due
largely to the high capital cost of the equipment required compared with traditional
steam distillation, much of which is already in place.
However, as can be seen from Table 12.5, subcritical water extraction does
have a number of advantages over supercritical CO
2
- most notably the ability to
extract green materials without drying and the lower operating costs. Greater use
of both of these extraction techniques will only emerge slowly and will be driven
by higher prices of conventional solvents, tighter legislation on solvent residues,
and consumer pressure to replace the use of solvents.
12.2.3 Microwave assisted isolation of essential oils
Microwaves are electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 0.3-300 GHz,
although domestic and industrial microwaves operate at 2.45 GHz to avoid
interference with radio communications. Microwaves possess electric and
magnetic fi elds that are perpendicular to each other and the electric fi eld














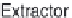







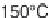
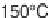
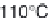





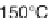
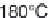















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search