Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
stability of foods when used as an additive, including: water-in-oil emulsions and
margarines (Pokorný
et al.
2001); and butter, butterfat, coconut oil and corn oil
(Nanditha and Prabhasankar 2009). Additionally,
β
-carotene has been shown to
exhibit synergistic antioxidant effects in oil-in-water emulsions when combined
with other carotenoids, such as bixin from annatto (Kiokias and Gordon 2003)
and when combined with
α
-tocopherol (Li
et al.
1995).
Carotenoids are very sensitive to the presence of metal ions, light, pH and heat
(Thyrion 1999).
5.3.4 Chelators
There are not many known natural antioxidants that work by chelating transition
metal ions and preventing them from initiating oxidation (hence the categorization
of 'preventative antioxidants'). Although many plant phenolics with multiple
phenolic groups (especially in the di-
ortho
position) can act both as radical
scavengers and metal chelators, there are some natural molecules that can stabilize
food with metal chelating being their main mode of action. The most common
ones are citric acid, phospholipids and amino acid/peptides/proteins. These are
discussed below.
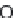
Citric acid
Citric acid is a natural chelator that can be found in a variety of fruits and
vegetables, such as lemons (Madhavi and Kulkarni 1996) (Fig. 5.13). It can be
made dispersible in oil while other food chelators, including synthetic
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and phosphate, generally cannot.
Citric acid was evaluated in the 1940s and 1950s in butterfat, vegetable oils,
shortenings, lard, fats and the phospholipid portion of milk (Stull
et al.
1951). Its
use has been studied in combination with primary antioxidants such as mixed
tocopherols (Lea 1944) and BHA (Magoffi n and Bentz 1949).
Citric acid has been studied in a variety of applications such as fats and oils,
fruit and vegetable products, and meat products. It slows down lipid oxidation,
browning, the discoloration of fruits, and the formation of nitric oxide hemoglobin
in cured meats as well as rancidity in ground beef and pork sausage (Madhavi and
Fig. 5.13
Citric acid.



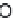
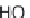




Search WWH ::

Custom Search