Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
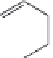
Fig. 5.4
Antioxidant mechanism of carnosic acid.
Sage (
Salvia offi cinalis L.
)
As with rosemary, the most active antioxidant ingredients in sage are carnosic acid,
carnosol and rosmarinic acid, and to a lesser extent rosmanol, rosmadial, genkawin
and cirsimaritin (Cuvelier
et al.
1996). Although many other antioxidant compounds
have been isolated and identifi ed from sage including 9-ethylrosmanol ether,
luteolin-7-
O
-
β
-glucopyranoside, 6-
O
-caffeoyl-
β
-
D
-fructofuranosyl-(2→1)-
α
-
D
-
glucopyranoside and 1-
O
-caffeoyl-
β
-
D
-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-
β
-
D
glucopyranoside,
the most active antioxidants are carnosic acid, carnosol and rosmarinic acid
(Yanishlieva
et al.
2006).
Sage is less commercially attractive than rosemary because of its cost and
inferior activity compared to the latter (Berdahl
et al.
2010). Nevertheless,
commercial attempts to produce sage have been pursued, and various commercially
decolorized and defl avorized sage extracts suitable for use in foods were produced
on a large scale in the late 1970s and early 1980s (Adegoke
et al.
1998). One food
product use unaffected by the high cost of sage extract is certain meat products
like breakfast sausages, where sage fl avor is integral to the product, and sage
extract provides both fl avor and antioxidant protection. Sage extract is an effective
antioxidant for various oils such as sunfl ower, rapeseed, palm and bergamot in
















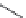




























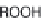








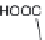



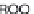




















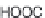






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search