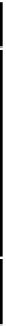Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
calorific value of the gas depends on the percentage composition of combustible gases such as
methane, and non-combustible gases such as carbon dioxide. The presence of carbon dioxide
results in reduced flame temperatures and burning rates, a narrower range of flame stability
and thus lower combustion efficiency (Qin et al 2001). The carbon dioxide is also regarded as
'inert', in that it does not combust and therefore does not contribute to the energy content of
the landfill gas.
B. U.S.E.P.A. Model - Landgem
1. Model description
The landfill gas emission model (LandGEM) developed by US EPA provides an
automated estimation tool for estimation of landfill gas emissions from municipal solid waste
MSW landfills (http://www.epa.gov/ttn/catc/products.htmlsoftware).
The model is based on a first order decomposition rate equation to estimate annual
emissions over a specified time period, described as follows:
n
1
M
⎛
⎞
=
∑∑
−
kt
Q
kL
e
⎝
i
⎠
ij
CH
o
10
4
(1)
i
==
1
j
.
0
Where,
Q
Annual Methane generation in the year of the calculation (m
3
/year)
=
CH
4
M
=
Mass of waste accepted in the year
I
(Mg)
L
Potential methane generation capacity of the waste (m
3
/Mg)
=
k
=
Methane generation rate (per year)
j
=
Waste type category (index)
i
= 1Year
n
=
(year of the calculation)- (initial year of waste acceptance)
Age of the j
th
section of waste mass
M
accepted in the i
th
year (decimal
i
t
=
years, e.g., 3.2 years)
1.1. Input Parameters
Main Input parameters required for LandGEM are as follows:
•
Annual Waste acceptance rate during the operation of the landfill (tons/year)
•
Start year and end year of the landfill operations
Assumed values of methane generation rate (
k
) and methane generation potential
(
•
L
)
•
NMOC concentration and methane content in landfill gas