Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
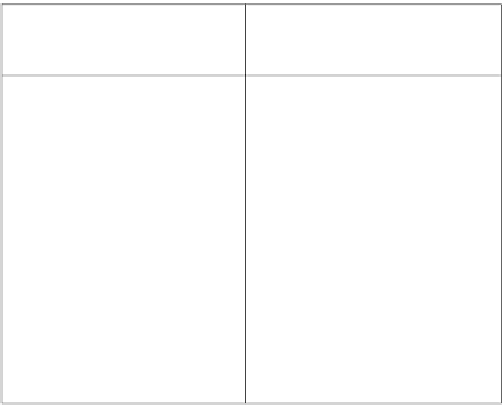
∆ T minimum = 10 K
Hot Streams
Cold Streams
T*
Interval
Tt
555
560
550
1
H1
515
520
510
2
385
390
380
3
H2
375
380
370
4
330
320
310
C2
5
310
300
305
C1
6
295
300
290
Hot Streams:H1;
F1Cp1= 10 kW/K
Cold Streams:C1; F1Cp1= 10 kW/K
C2; F2Cp2= 5 kW/K
H2;
F2Cp2= 5 kW/K
Figure 6. The Temperature Interval Diagram
2. Constructing Tables of Exchangeable Heat Loads and Cooling Capacities
2.1. Determining individual heating loads and cooling capacities of all process streams
for all temperature intervals using this formula:
Qnm = F1Cp1* (Ts-Te) in energy units (kW)
Ts is the interval start temperature and
Te is the interval end temperature
“n” is stream number and “m” is the interval number
Example 1:
Interval # 1 in the hot section:
The interval start temperature is 560 K
The interval end temperature is 520 K
Q11 (Q for stream #1 in interval #1)= F1Cp1*(560-520)
Since there is no H1 stream in this interval, hence, F1Cp1=0.0
Q stream # 1(exchangeable load) in this interval = 0.0*(560-520) = zero
Example 2:
Interval # 2 in the hot section:
The interval start temperature is 520 K
The interval end temperature is 390 K
The flow specific heat F1Cp1= 10 kW/K
Then,
Q stream #1(exchangeable load) in interval #1= 10*(520-390) = 1300 kW