Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
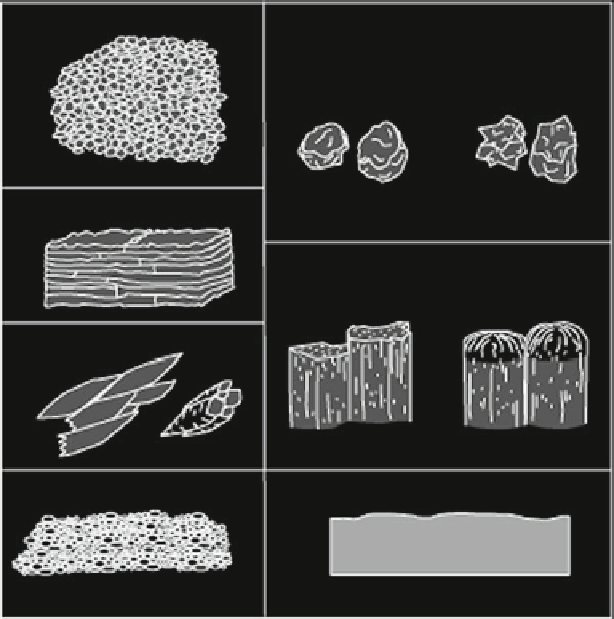
Granular
Blocky
(Angular)
(Subangular)
(Soil aggregates)
Platy
Prismatic
Columnar
Wedge
Single Grain
Massive
(Mineral/rock grains)
(Continuous, unconsolidated mass)
Fig. 4.10 A diagram of the types of soil structure (Published with kind permission of US
Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service from Schoeneberger
et al. (
2002
). Figure is public domain in the USA. All Rights Reserved)
4.8 Soil Organic Material
4.8.1 Overview
Soil microbes use carbon (C) compounds found in organic material as an energy
source. However, the rate at which organic C is utilized by soil microbes is
considerably lower in a saturated and anaerobic environment than it is under aerobic
conditions. Therefore, soils that are saturated the entire growing season may accu-
mulate partially decomposed organic material. The result in wetlands is often the
development of O horizons of various thicknesses or dark organic-rich mineral
surface layers. Three types of O horizons are recognized and distinguished by the
level of organic material decomposition. Oa indicates highly decomposed organic
material, Oi is slightly decomposed, and Oe is intermediate in decomposition.