Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
CHAPTER 7
Polymer Basics
“Mer” is derived from the Greek word “meros” meaning part. Therefore, a
monomer means one part or one unit; dimer means two units; oligomer means
a few units; and polymer means many units. A polymerization involves
the reaction of a monomer to connect many monomer units. If the reaction
is additive, where one monomer adds to the next as in the polymerization
of styrene, the polymer is called an addition polymer. Polymerizations of
olefins, such as ethylene, propylene, vinyl chloride, or styrene, are addition
polymerizations. In an addition polymer, all of the atoms of the monomer
remain in the polymer. If the monomers are connected in a condensation
reaction such as when a carboxylic acid and an alcohol react to remove
water and form an ester linkage, then the polymer is called a condensation
polymer. Recognize that in this type of polymer all of the monomer atoms
are not incorporated into the final polymer.
One common method used to polymerize olefins is a free radical
polymerization. For example, polystyrene can be prepared by heating styrene
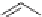
with a small amount of a radical initiator such as benzoyl peroxide. Benzoyl
peroxide forms the benzoyl oxy radical and the phenyl radical [1]; for
simplicity only the benzoyl oxy radical is shown.
O
O
2 PhCO
2
O
O
O
O
Ph
PhCO
2





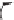


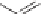




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search