Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
the purchase price of Brent oil was $10 - $25 higher than WTI. However,
in September of 2008, when the U.S. was undergoing the financial crisis
induced by subprime mortgages, the spread spiked down with WTI trading
at a purchase price of about $22 higher than Brent. In January of 2014, Brent
was trading about $10 per barrel higher than WTI. The major use of oil is
for gasoline and we can see the price fluctuations at the gas pump. However,
many chemicals are based upon petroleum and their availability and cost is
also influenced by the cost of oil.
The oil is refined, a process which converts the oil into usable products,
mainly gasoline, but also several other chemical feedstocks. In the refining
process, a continuous distillation is employed. Oil is continuously fed to a
distillation column and different fractions are continuously removed from
various heights in the column. Low boiling fractions are removed from the
top, high boilers from the bottom and several other fractions from various
places along the column. The lowest boiling fraction (light fraction) is a gas
mixture and high boiling fractions are used as fuel oil or even for asphalt.
An intermediate fraction is called naphtha. This can be further categorized as
light naphtha or heavy naphtha. Naphtha is processed further by cracking or
reforming to gasoline and other useful chemical feedstocks.
Cracking, as the name implies, breaks the molecules into smaller
molecules, typically with more unsaturation. This chemical breakdown is
done at high temperatures in the presence of a catalyst, hence the term,
“catalytic cracking.” One subset of catalytic cracking is the FCC (fluid
catalytic cracking) process which uses a zeolite powder. Catalytic cracking
in the presence of hydrogen is called hydrocracking.
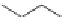
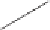
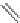
We can start to get a sense of the chemistry by considering how n-heptane
might be cracked. It is a radical mechanism and by heat, enough energy is
supplied to break bonds.
H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
·
·
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
Heptane
Propyl radical
Butyl radical
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
+H
·
·
H
+
H
H
H
H
H
H
Propylene
Ethylene
By breaking the C3-C4 bond, we create a propyl radical and a butyl
radical. The propyl radical can decompose to propylene and a hydrogen
radical. The butyl radical can form ethylene and an ethyl radical. The formed



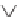

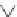

















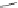










Search WWH ::

Custom Search