Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Pharmaceuticals, Inc.) and isocarbazid (Marplan
®
, Validus Pharmaceuti-
cals). They also suppress tyramine uptake. In response to diet-related surges
of tyramine, some patients experienced sudden increases in blood pressure
that caused fatal brain hemorrhages [51]. Newer antidepressant medications
are based upon the inhibition of serotonin reuptake.
H
3
C
H
3
C
N
CH
3
N
CH
3
S
Dothiepin
Amitriptyline
CH
3
CH
3
N
N
O
N
H
H
CH
O
CH
3
Selegiline
Isocarboxazid
Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is biosynthesized
from tryptophan and is a neurotransmitter. Serotonin plays an important role
in many behaviors including sleep, appetite, memory, and mood [52]. Peo-
ple with depressive disorders exhibit low levels of serotonin in the synapses.
Protonated serotonin binds to a serotonin reuptake transporter protein, some-
times referred to as the serotonin transporter (SERT) and is then moved to an
inward position on the neuron and subsequently released into the cytoplasm.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) bind with high affinity to the
serotonin binding site of the transporter. This leads to antidepressant effects
by increasing extracellular serotonin levels which in turn enhances serotonin
neurotransmission [53]. The SSRI class of antidepressants has fewer side
effects than the monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
CO
2
H
NH
2
NH
2
HO
HO
N
H
H
Serotonin
Tryptophan
There are several SSRI inhibitors. Their chemical structures are different
but they have similar modes of action, namely binding to the SERT. How-
ever, they have different pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-life, and
differences in adverse effects and drug interactions [54]. Fluoxetine was the
first drug of the class, approved in the U.S. in 1987. It is a chiral molecule and
the racemic mixture is used as the hydrochloride salt (Prozac
®
, Lilly). It has
been approved and marketed in more than 90 countries and used by more than
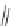




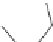



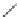

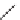







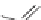
















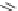













Search WWH ::

Custom Search