Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
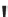
CH
3
HS
O
N
CH
2
O
2
H
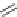
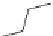
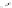
Captopril
The second and largest class of ACE inhibitors replaced the thiol linkage
and the potentially related side effects caused by the thiol group by using a
carboxylic acid to bind to the zinc. Lisinopril (Zestril
®
, AstraZeneca) is an
example of this type of ACE inhibitor. In some cases an ester prodrug is used
which hydrolyzes in vivo to the carboxylic acid. Enalapril and quinapril are
examples of ACE inhibitor prodrugs.
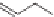
NH
2
CO
2
Et
O
N
H
CO
2
Et
CH
3
CO
2
H
N
CO
2
H
O
O
N
H
H
N
CO
2
H
N
CO
2
H
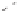
Enalapril
Lisinopril
Quinapril
Lisinopril can be prepared [29] from the trifluoroacetamide derivative of
lysine. Reaction with phosgene gives the N-carboxyanhydride which reacts
with proline. Reductive condensation of the amine is followed by hydrolysis
of the trifluoracetamide protective group to give lisinopril.
O
O
O
CO
2
Et
O
F
3
C
F
3
C
F
3
C
NH
NH
NH
1. L-proline/KOH
2. H
2
SO
4
COCl
2
O
O
O
H
2
Raney Nickel
H
2
N
H
2
N
HN
O
CO
2
H
OH
O
O
F
3
C
NH
NH
2
CO
2
Et
CO
2
H
O
O
NaOH
N
H
N
H
N
N
CO
2
H
CO
2
H
Lisinopril




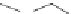







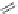
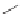


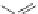












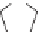











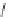



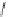


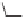

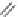

























































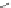

Search WWH ::

Custom Search