Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
in polyurethanes and in polyphenylene oxide. A type of flame retardant useful
for polycarbonate are salts of sulfonic acids [19, 20] such as the potassium salt
of aromatic sulfonic acids, exemplified by potassium toluene sulfonate. These
are thought to promote a char layer in the flame.
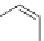
SO
3
K
CH
3
Potassium p-toluene sulfonate
A third type of flame retardant interferes with the chemical reactions that
maintain the combustion. These are based upon halogenated compounds,
often brominated aromatic compounds. These flame retardants are somewhat
thermally labile and release bromine radicals that quench the radical chain
reactions during the combustion and flame spreading processes. Antimony
oxide, Sb
2
O
3
, is often added because it has a synergistic effect with the
brominated flame retardant. Antimony oxide increases the rate of release
of halogens via the formation of antimony halides and oxyhalides during
combustion [21]. The bromine radical abstracts a hydrogen atom to form
HBr, which can then quench hydrogen radicals, forming hydrogen and a
bromine radical. HBr can also quench a hydroxyl radical, forming water and a
bromine radical. The hydrogen radical is responsible for the chain-branching
free radical reactions in the flame and the hydroxyl radical is responsible
for the oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide which is a highly
exothermic reaction and responsible for the larger part of the heat generation
in the flame [22].
Because of the synergistic effect of antimony oxide, it is almost always
added with the halogenated flame retardant into the formulation. All halo-
genated compounds can act as flame retardants, so PVC with added antimony
oxide can be flame retardant. However, aliphatic halogenated compounds are
less common than aromatics because of their ability to undergo dehydro-
halogenation during processing, especially when used for polymers that are
processed at high temperatures. Brominated aromatic compounds are stable
during processing but readily decompose in the flame. The more thermally
stable chlorinated aromatic compounds are slower to decompose in the flame
and are less effective in most applications. Some brominated flame retardants
are shown.







Search WWH ::

Custom Search