Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
2.3
Infeasibility Driven
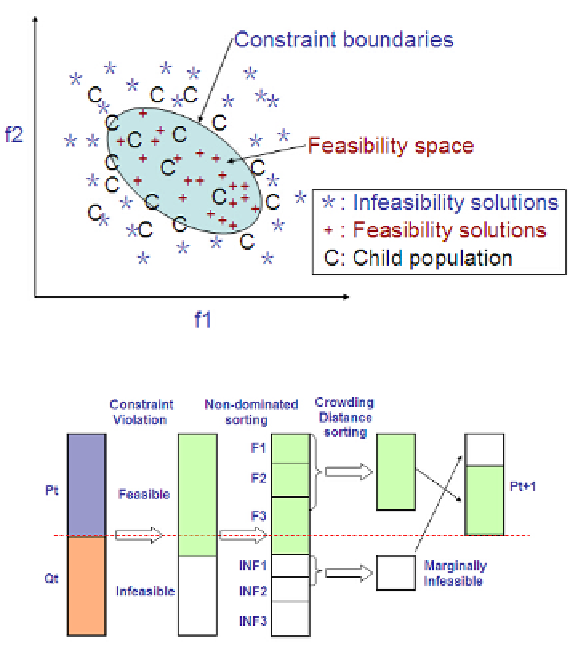
Infeasibility driven (ID) is a mechanism for constrained handling problem first pro-
posed in Infeasibility Driven Evolutionary Algorithm (IDEA) [7]. ID first evolves a
child population and merges the parent population with the child population into a
new extended set. Then, the combined population is divided into a feasible set and an
infeasible set by constraint violations. When creating the second generation, a certain
percentage of feasible solutions (×) and marginally (say, 20%) infeasible solutions
(
) are adopted into the new population to evolve. As the presence of infeasible solu-
tions in each population might drives the child populations (C) onto the constraint
boundaries where the optimal solutions may exist, as indicated in Figure 1. In infeasi-
bility driven mechanism, infeasible and feasible solutions need to be ranked using
original objectives and constraint violation. One ranking scheme is called infeasibility
driven ranking. As is shown in Figure 2, in CDP the feasible and infeasible sets are
separately ranked using nondominated crowding sorting. We need to define a parame-
ter
ʱ
that is used to identify the proportion of the infeasible solutions to be retained
in the population. If the population size is N, the number of feasible and infeasible
solutions in the population are respectively denoted as (1 −
ʱ
ʱ
) × N and
×N.
Fig. 1.
Illustration of Infeasibility Driven (ID) Mechanism
Fig. 2.
Infeasibility Driven Ranking
Search WWH ::

Custom Search