Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
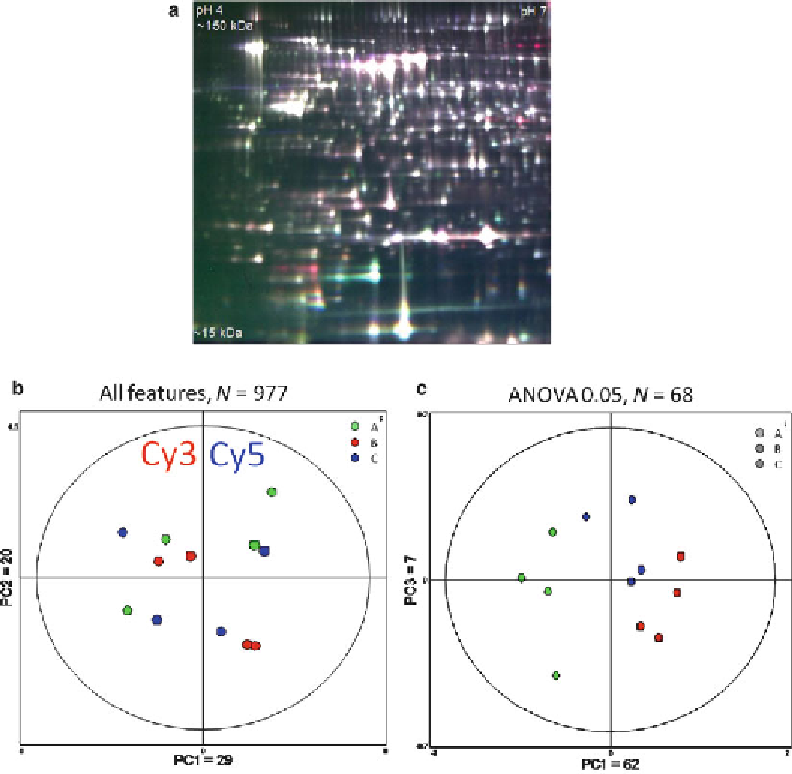
Fig. 3. PCA showing an extremely low signal-to-noise ratio.
Helicobacter pylori
cultured under three different experimental
conditions: A, B, and C. The experiment was repeated four independent times, resulting in 12 samples coresolved across six
DIGE gels along with a Cy2-labeled internal standard. (
a
) Representative DIGE gel from the 6-gel set. (
b
) PCA performed on
the unfi ltered 977 features matched across all six gels failed to organize the samples based on the anticipated biological
manipulation but indicated a low level of variance (PC1 = 29%) that organized the samples based on Cy3/Cy5 dye-labeling
bias. Such dye bias is known to exist; that it appears here indicates not only that the biological signal is not detected but also
that the technical noise is similarly low because only dye bias, and not something else, is infl uencing PC1. (
c
) Refi ning the
PCA to 68 features that exhibited a signifi cant change between any group relative to the others (ANOVA
p
< 0.05) now begins
to reveal some biologically relevant ordering of the samples based on the fi rst two principal components.
demonstrates that the weak signal is present once the background
noise (dye bias) is removed by imposing a biologically infl uenced
fi lter over the data.
This last example depicts a worst-case scenario where, without
inspecting the global variation with PCA, the experimental results
might be misinterpreted. In this case, a primary mammalian cell
3.7. Example 4: Low
Signal, High Noise
Search WWH ::

Custom Search