Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
ICy3
ICy5
+N
+N
N
N
HN
HN
I
I
O
O
C
34
H
45
N
3
OI
C
34
H
43
N
3
OI
MW: 638.6 Da
Excitation:540nm
Emission: 590nm
MW: 636.6 Da
Excitation:620nm
Emission: 680nm
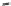
Fig. 2. Structure of the matched ICy3 and ICy5 iodoacetylated cyanine dyes. Chemical
formulas, molecular weights, and excitation/emission wavelengths are shown.
changes in the redox status of proteins in 2D gels (
9, 10
). For
example,
N
-(biotinoyl)-
N
¢ -(iodoacetyl) ethylenediamine was used
for detecting selenium metabolite targets with labeled proteins
detected using HRP-streptavidin and chemiluminescence (
11
). In
another approach to monitor protein thiol oxidation in cultured
cells, reduced thiols were fi rst blocked with
N
-ethylmaleimide,
then any oxidized thiols were reduced with dithiothreitol and
subsequently labeled with 5-iodoacetamidofl uorescein prior to
2DE and fl uorescence detection (
12
). Such labeling approaches,
especially using biotinylated derivatives, also allow affi nity enrichment
of the labeled pool of proteins for improved sensitivity of gel- and
MS-based analyses.
A major drawback of these single labeling methods is reduced
quantitative accuracy and precision due to the inherent variation of
2DE. To overcome this, we have developed a pair of iodoacety-
lated cyanine dyes (ICy3/5; see Fig.
2
) for cysteine-labeling 2D
DIGE to monitor redox-dependent changes on protein thiols and
have tested the method in a model cell system of human mammary
luminal epithelial cells exposed to H
2
O
2
(
13
) and in plasma prepa-
rations disinfected by UVC irradiation (
14
). It is expected that any
differences in labeling are caused by changes in the content of reac-
tive thiol groups. Proteins displaying differential labeling on 2D
gels are then picked for identifi cation by MALDI-TOF MS peptide
mass fi ngerprinting or LC-MS/MS with further validation of
changes carried out by 1D and 2D immunoblotting. As the outlined
protocol directly measures the labeling of free thiols between
protein samples, changes in the expression levels of thiol-containing
proteins are also expected to give rise to an altered ICy dye signal.
For this reason, we recommend running a lysine-labeling experiment
with NHS-cyanine dyes in parallel to aid in the discrimination of
expression changes vs. redox-dependent changes. A detailed
protocol for this is provided elsewhere in this volume.



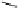







































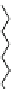






Search WWH ::

Custom Search