Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Coffee
Sugar cane
Rice
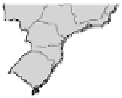
Fig. 2.1.
Map of Brazil showing the regions Minas Gerais, Sao Paulo and Rio Grande do
Sul which are respectively leading coffee, sugar cane and rice production (Source:
www.limasolucoes.com.br/images/mapaBrasil.gif)
2.3 Materials and Methods
Four types of Brazilian biomass - rice and coffee husks, sugar cane bagasse and
sawdust from
Eucalyptus sp.
wood - were investigated. The residues were col-
lected in the Federal State of Minas Gerais, where the Federal University of
Viçosa, a partner university, is located. The coffee husks were from a large-scale
farm located in the region called Zona da Mata. Rice husks and sugar cane ba-
gasse were also collected in the same region, although from small-scale agricul-
ture. The local furniture and carpentry industry uses mostly
Eucalyptus sp.
wood,
producing a high quantity of sawdust, which was also used in the experiments.
The research consisted of three steps:
•
Collection, drying and transporting of samples
•
Analysis of biomass properties
•
Pelleting
During the months of May and June, the residues were collected, stored and dried
in order to decrease moisture content and avoid decomposition. Thereafter, the
samples were packed and transported to Germany with a moisture content value of
approximately 13%. The analysis of the transported material was carried out in
August at the BTU Cottbus. This investigation covered some chemical-physical
aspects, such as: moisture content, ash content, heating value and ash melting
point. These preliminary results are important to characterize the efficiency of the
pellets as a fuel. Although the elementary analysis and the emission analysis of
CO
2
, SO
2
, NOx and dust are not included here, further investigations are planned.
Thereafter, the agglomeration properties of the residues have been investigated
by pellet formation. The pelleting process was performed with the Laborkompak-
tor Bepex L 200 / 50 G + K compressor producing approximately 20 kg of pellets
per hour. This was carried out after crushing and moistening (17.5%) the material.









































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search