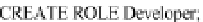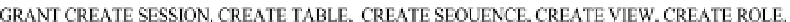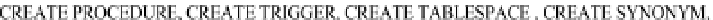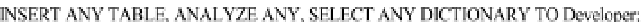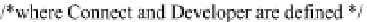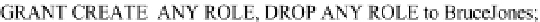Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Note:
To create a role, you need to have the
Create-Any-Role
system privilege
(the
Any
is optional; if supplied, you can create a role in any schema; if omitted, you can
create roles in your schema only). Only role owners and users with
Alter-Any-Role
and
Drop-Any-Role
system privileges can modify or delete a role.
Example 9:
Create a role called
Developer
with appropriate privileges and grant the
role to Bruce Jones:
You can use terms such as ANY, ALL, NONE and EXCEPT in assigning privileges.
Example 10:
The following examples illustrate the use of these keywords:
13.2.3 Access to the System Data
Access to system data can be managed in one of three ways:
•
Through object privileges
•
Through logical views
•
Through intricate database design
Security via Object Privileges
Object privileges apply to specific database objects and are sometimes referred to as
SUDI (select, update, delete, and insert) privileges. Below (Figure
13-10
) is a list of
possible object privileges and the relevant types of database object to which they apply: