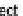Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 8-4b.
Graphical Representation of Optimized Solution to Example 12
8.6 Domain Oriented Relational Calculus
Domain related relational calculus involves the manipulation of
domain variables
instead of tuple variables (these must be defined similar to tuple variables). It supports an
additional form of comparison called the membership condition. A member condition
takes the form
R(A:V {,A:V}) where
R is a relation, A is an attribute, V is a domain variable or a scalar value (also called
a
literal
). The condition evaluates true iff $ a tuple in R having specified values for the
specified attribute.
Example 15:
Example 16: