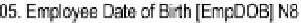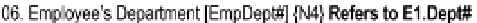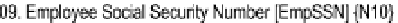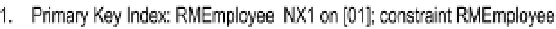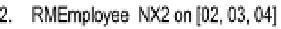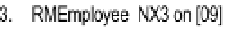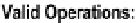Database Reference
In-Depth Information
The system must also facilitate various user (external) views through logical
interpretation of objects. This must be developed using the DBMS and/or whatever
software development tool is being used. Note that if the O/ESG methodology
(discussed in section 5.8) is employed, you will be well on your way with the user
interface specification.
Example:
By the way of illustration, let us revisit the O/ESG for the partial database
specification of the manufacturing firm, discussed in the previous chapter (section 5.8).
Figure
6-1
shows a repeat of the O/ESG for the
Employee
entity. According to the
figure (adopting the conventions from section 5.8), this entity could be implemented
as a relational table named RMEmployee_BR. The user interface should anticipate and
support various logical views on this relational table. Following are some examples:
•
Employees arranged by Name
•
Employees arranged by Telephone Numbers
•
Employees arranged by Departments
•
Employees arranged by Social Security Number
Figure 6-1.
Excerpt from the Partial O/ESG for Manufacturing Environment