Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
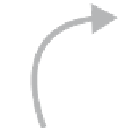
Fig. 5.4
The force exerted
by the biceps muscle is
represented by the vector
that departs from the point
of muscle attachment to the
bone and follows the muscle
direction
muscle force
biceps
Fig. 5.5
Models of
articulation (
a
) ball
and socket type;
(
b
) hinge type
a
b
it enables the human being to move himself and to displace with considerable
effort, that is, performing mechanical work.
The shape of bones and their internal structure combine lightness and strength.
Articulations, well lubricated, slide smoothly without friction, ensuring the most
diverse movements.
5.5.2 Articulations and Joints
Joints are places where the bones touch. Some are immovable, connecting the bones
firmly (joints of the skull). Articulations are movable joints that enable movements.
Two examples of articulations are shown in Fig.
5.5
:
Ball and socket type, such as the shoulder joint that allows rotational motion of
the arms
Hinge type, such as the knee joint and the elbow joint that allows motion in a
plane
The articulated bones have soft cartilage at their articulation extremity. In
addition, the region is filled with viscous fluid that guarantees good lubrication.