Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
d
90°
D
C
A
B
F
3
F
1
F
2
R
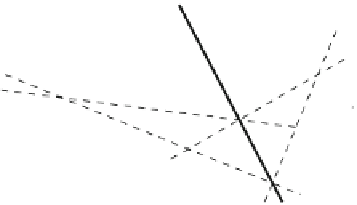
The first thing to do is to transport the force vectors to do a vector addition. We
obtain for the magnitude of the resultant the value
R
¼
26.3 N.
Next, from the point
P
, we draw the polar rays and then transfer them to the
diagram of forces. The point of intersection between the first and the last polar rays
defines the point where the line of action of the resultant force must pass. Then, the
arm of the resultant can be obtained using the scale:
d
⊥
¼
16.5 cm
¼
0.165 m.
Hence, the net torque due to the resultant force about the axis at O is
M
R
¼
Rd
⊥
¼
(26.3 N)(0.165 m)
¼
4.3 N m.
Direction of rotation: clockwise
Exercise 2.5
Determine the resultant of the coplanar forces and its torque about the
axis through O of the figure of Exercise 2.5 by the method of funicular polygon.
Utilize the following scales:
F
1
axis O
F
2
1 cm in the drawing
¼
10 N for the force.