Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
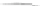
Fig. 2.6
Two forces are
applied on the bar. The net
torque is the sum of the
torques due to each force
F
1
axis
d
1
d
2
F
2
lever arms
When a body is subjected to more than one force, we have to find the torque due to
each force and add them to obtain the resultant torque. Figure
2.6
shows two forces
acting on a bar. The resultant torque about the axis at pivot point O is given by
M
¼
F
1
d
1
F
2
d
2
:
(2.2)
The direction of rotation is defined by the magnitude of forces and the lever arms
involved. If the first (second) term of (
2.2
) is smaller than the second (first) term, the
resultant torque will produce clockwise (counterclockwise) rotation of the bar.