Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
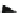
Fig. 1.7
Addition of forces
F
1
and
F
2
which gives the
resultant
R
by the method of
parallelogram
F
1
F
1
parallel to F
2
R
F
2
parallel to F
1
F
2
y
a
b
F
1y
y
F
2
F
2y
F
2y
R
F
1
F
1y
F
2x
x
x
F
1x
F
2x
F
1x
Fig. 1.8
Addition of vectors
F
1
and
F
2
decomposed in
F
1
x
,
F
1
y
and
F
2
x
,
F
2
y
, respectively, by the
method of components in (
a
). In (
b
) the algebraic sum of
F
1
x
with
F
2
x
and
F
1
y
with
F
2
y
was done in
order to obtain the resultant
R
resultant vector obtained with the sum of several vectors will correspond to a vector
in which its
x
(
y
) component is the algebraic sum of
x
(
y
) components of all vectors.
Once the components of the vector are found, the magnitude of the resultant vector
can be obtained by applying the Pythagorean theorem. This method is shown in
Fig.
1.8
, where the forces
F
1
and
F
2
are added.
1.5.4 Algebraic Method
The magnitude of the sum vector can also be calculated by the law of cosines,
applied to the triangle formed by the forces
F
1
,
F
2
, and
R
, represented in Fig.
1.9
:
p
F
1
2
F
2
2
R
¼
þ
þ
2
F
1
F
2
cos
θ
:
(1.1)