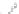Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
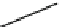
Fig. 1.1
(
a
) A small
horizontal force pushes an
object to the right. (
b
)A
larger force pulls an object
at an angle of 45
with the
horizontal to the right. Both
forces are applied, for
example, by the hand of a
person
a
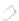
b
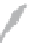
Fig. 1.2
Two examples of
forces acting at a distance.
A magnet attracts a piece of
iron, and a large mass
M
and
a small mass
m
experience a
gravitational attractive
force, in a different way
compared with the contact
forces shown in Fig.
1.1
mass
m
mass
M
We also must consider forces that act at a distance, such as electric, magnetic,
and gravitational forces, shown in Fig.
1.2
. In these cases, the source of the force is
not in contact with the body on which it acts, and the force is called a field force.
In this chapter, we deal with three types of force: gravitational force, muscle force,
and friction. The actions of gravitational and muscle forces cause joint compression
and joint tension, compression, or pressure (force per unit area) on the tissues or
organs of a body.