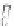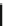Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6.5 Forces on the Hip
When we walk, we are briefly standing erect on one leg, which changes at every
footstep. At this moment, the center of gravity must lie on an imaginary line passing
simultaneously through the vectors weight force
W
of the body and normal force
N
,
the foot that touches the ground. At each footstep, the articulation of the hips
(acetabulum of the femur that is of the ball-socket type) exerts on the head of the
femur of the leg that supports the weight, a contact force
C
larger than twice the
body weight force. The hip abductor muscle force
F
is exerted by the muscles
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and
tensor of fascia lata femoris
on the great
trochanter of the femur. V.T. Inman wrote in 1947 the paper
Functional Aspects of
the Abductor Muscles of the Hip
in the J. Bone Joint Surg. 29 607-619. The results
of the measurements of forces exerted by the abductor muscles were presented in
this paper. He obtained the value of 70
for the angle of the abductor force to the
horizontal and the average distances involved in the leg of an adult, as illustrated in
Fig.
6.1a
. Figure
6.1b
shows a simplified geometric model with the applied forces
on the inferior right limb with the foot on the floor. Thus, when we walk, the
magnitude of the contact force
C
changes drastically, according to the body weight
sustained by one foot or the other alternately.
When a person walks, the line of action of the weight force that passes through
the center of gravity is placed instinctively on the foot which is on the floor. When
we walk normally, this process occurs automatically, but the equilibrium becomes
disastrous when we try to walk very slowly, mainly with our eyes closed. Our body
a
b
F
C
F
C
7
0
°
7
0
°
O
Fig. 6.1
(
a
) An adult
standing on his right foot, in
static equilibrium. The
forces and the distances
involved are indicated.
P
is
the weight of the set thigh-
leg-foot and
N
, the normal
reaction to the weight force
W
of the body. (
b
) Sketch of
the geometric model of the
leg of (
a
)
P
P
N
N
3 cm
3 cm
7 cm 11 cm
7 cm 11 cm