Database Reference
In-Depth Information
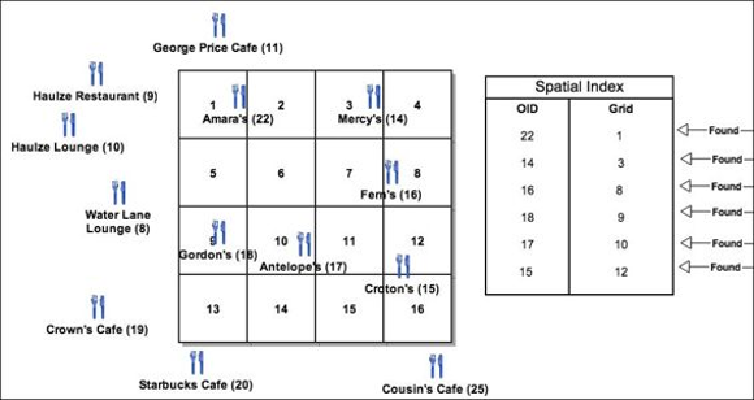
Spatial indexing creates small square grids in the entire feature class extent and updates
the relationship between each grid and the features inside that grid. This information is
stored in a separate table, which speeds up searching as shown in the following figure.
Geodatabases simply scan the spatial index grid table. Those grids with no features are
automatically skipped, which saves query execution time. We will get the same result, that
is, 22, 14, 16, 18, 17, and 15, but much faster.