Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
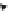
Hexokinase
Glucose
Glucose-6-phosphate
Hexosephosphate isomerase
ATP
ADP
Fructose-6-phosphate
ATP
ADP
Dihydroxyacetone pghosphate
Phosphofructokinase
Triose phosphate
isomerase
Aldolase
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
NAD
NADH
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase
1,3-Diphosphoglycerate
ADP
Glycerate-3-phosphate kinase
ATP
3-Phosphoglycerate
2-Phosphoglycerate
Phosphoglycerate mutase
NAD
NADH
Enolase
ADP
ATP
Acetaldehyde
Ethanol
Pyruvate
Phosphoenol pyruvate
Alcohol
dehydrogenase
Pyruvate
decarboxylase
NAD
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Anaerobic metabolism
CO
2
NADH
Acetyl CoA
Oxaloacetate
Malate
dehydrogenase
Citrate
Citrate synthse
Aconitase
NADH
NAD
Malate
Isocitrate
CO
2
NAD
Citric acid cycle
Fumarase
NADH
Isocitrate
dehydrogenase
NAD
FADH
2
FAD
Fumarate
α
-Ketoglutarate
NADH
ATP ADP
CoA-SH
Succinate
dehydrogenase
Succinate
Succinyl CoA
CO
2
Succinate thiokinase
CoA-SH
Catabolism of sugars through glycolytic pathway and citric acid cycle.
Fig. 3.4
conditions, pyruvate can be metabolized to ethanol, which is a byproduct in several ripening
fruits.
There are two key regulatory steps in glycolysis: one mediated by phosphofructokinase
(PFK) and the other by pyruvate kinase. In addition, there are other types of modulation
involving cofactors and enzyme structural changes reported to be involved in glycolytic







































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search