Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Ethylene receptor
C
2
H
4
X
Membrane
1-MCP
PLD
Wax
Esters
X
PL
PA
PL
ACAT
Hexanal
Hexanol
Hexanal
Retailoring
desaturation
PAP
HPL
LOX
SCFA
Fatty acyl
CoA
DG
FA
LAH
Malonyl
CoA
Glycolysis
Acetyl
CoA pool
Sugars
Acetoacetyl
CoA
HMG CoA
Pentose
phosphate
pathway
Mevalonate
NADPH
IPP
DMAPP
Erythrose
4-phosphate
Pyruvate
Isoprenoids
Terpenes
Phenyl propanoid
pathway
(
α
Farnesene)
GH
DHA
NADP
+
GSH
DHA
Flavonoids
NADP
+
NADPH
Chalcone
MDHA
GSSG
NADPH
MDHA
ASA
Anthocyanins
O
2
SOD
APX
O
2
O
2
−
O
2
−
H
2
O
H
2
O
+
-
POX
Alternative
sources
2H
+
H
2
O
CAT
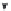
Fig. 21.3
A schematic representation of interrelated pathways and targeted inhibition of catabolic path-
ways. ACAT, alcohol acyl CoA acyl transferase; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; ASA/MDHA/DHA, ascor-
bate/monodehydroascorbate/dehydroascorbate; CAT, catalase; DG, diacylglycerol; DMAPP, dimethylallyl py-
rophosphate; FA, fatty acids; GR, glutathione reductase; GSH/GSSG, reduced/oxidized glutathione; HMG-CoA,
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA; HPL, hydroperoxide lyase; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; LAH, lipolytic acyl
hydrolase; LOX, lipoxygenase; MDHAR/DHAR, monodehydroascorbate reductase/dehydroascorbate reductase;
PA, phosphatidic acid; PAP, phosphatidate phosphatase; PL, phospholipid; PLD, phospholipase D; POX, peroxi-
dase; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids; SOD, superoxide dismutase.
21.5 Nutritional components in fruits and their changes
during storage
Fruits and vegetables are major sources of vitamins, minerals, polyphenols, antioxidants, and
dietary fibers. Their nutritional and health beneficial properties are increasing their demand
among consumers. Innumerable studies suggest that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables









































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search