Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Sucrose
Photosynthesis
Glucose
Glucose-1-phosphate
Starch
Pentose phosphate
pathway
Glycolysis
ATP
Hexokinase
NADP
NADPH
Glucose-6-phosphate
6-Phosphogluconate
NADP
NADPH
ADP
Glucose-6-phosphate
dehydrogenase
6-Phosphogluconate
dehydrogenase
CO
2
Ribulose-5-phosphate
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
NADPH pool
Pyruvate
Glyceraldehyde-3-
phosphate
Sedoheptulose-7-
phosphate
NAD
NADH
Pyruvate
dehydrogenase
Isoprenoid pathway
Acetyl CoA
Transaldolase
Fructose-6-phosphate
Erythrose-4-phosphate
Citric acid cycle
Phenyl propanoid
pathway
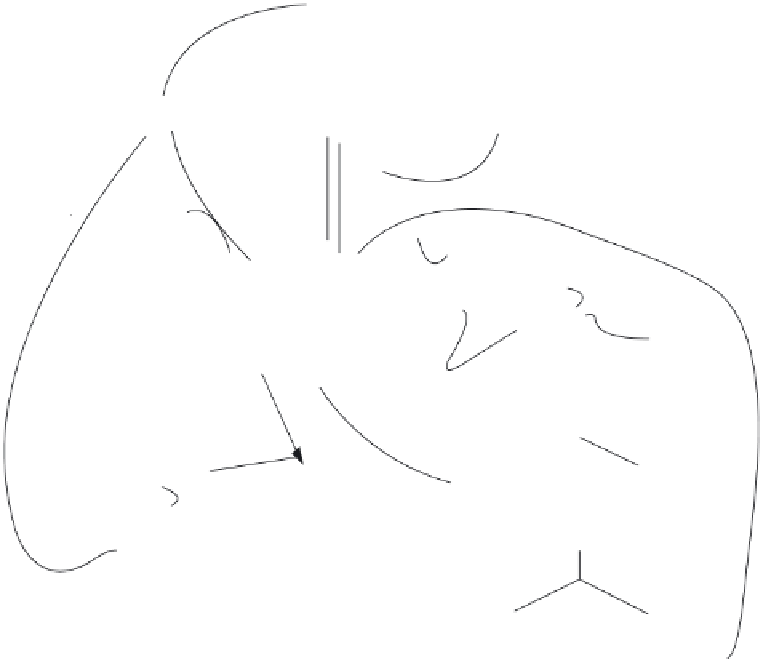
Fig. 21.1
Carbohydrate metabolism in fruits. Starch is catabolized to sugars that undergo glycolysis and pentose
phosphate pathway. Pentose phosphate pathway provides carbon and reducing power (NADPH) for the synthesis
of flavonoids through phenyl propanoid pathway.
21.4.2 Biosynthesis of isoprenoids
Isoprenoids are secondary plant products that are derived from primary metabolites. Al-
though there are several kinds of secondary plant products, the levels of isoprenoids, ester
volatiles, and anthocyanin components determine the fruit quality to a large extent. Iso-
prenoids are synthesized from two pathways: classical mevalonate (MVA) pathway and
1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) pathway. These two pathways provide precursors,
isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and its isomer dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), for
the synthesis of isoprene (Liu et al., 2005b; Paliyath and Murr, 2006). Mevalonate pathway is
localized in the cytosol, and DXP pathway occurs in the chloroplast. In mevalonate pathway,
three acetyl-CoA molecules undergo condensation to produce 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl
CoA (HMG-CoA), which forms mevalonic acid (MVA) in the presence of the enzyme

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search