Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
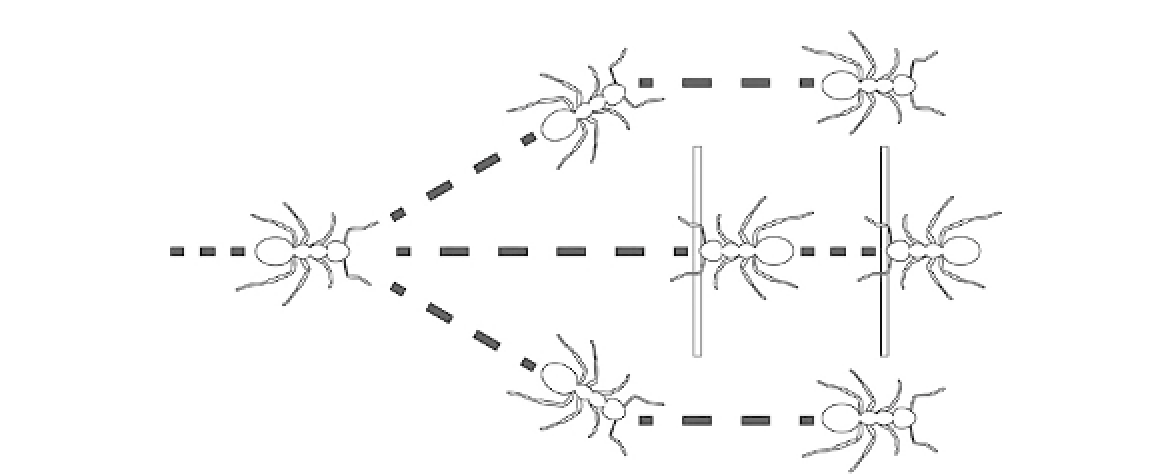
FIGURE 13.7
Basic principle used by army ants to form distinct traffic lanes. Outgoing ants without cargo have the duty
to give way to the returning ants carrying prey. Drawing based on the description in Ref.
28
.
Nouyan and colleagues
[33]
performed an
experiment with up to 12 small physical robots
that were given the foraging task to move a prey
to a home position called the
nest
. Movement of
the prey required concurrent physical handling
from more than one robot. The single robots
physically attached to each other in order to pull
the prey. The robots only had a small perceptual
range and would therefore not be able to find
their way back to the nest on their own. They
relied on contact with other robots that were
within their range. In most of their experiments,
where the group size was sufficiently large, the
robot swarm group succeeded in retrieving the
prey to the nest.
(2) sealing the damage (called
secondary hemosta-
sis
) so that the plug will last until the wound is
healed, and (3) healing the wound. In humans
(and other animals), specialized cells cover the
damage in a blood vessel through a cascade of
events, as explained by Purves and colleagues
[34]
. When the inner membrane of the vessel
(
endothelium
) is damaged, the blood comes in
contact with collagen fibers in the tissue. This
activates small cell fragments in the blood called
platelets
(thrombocytes), which swell become
sticky, and then release several clotting fac-
tors. The clotting factors activate more plate-
lets, which together form a plug. Furthermore,
they initiate the formation of fibrin fibers that
form a cloth which seals the vessel and acts as
a scaffold for the healing, where scar tissue is
built up. Fibrin formation involves a sequence
of actions. The clotting factors activate the pro-
enzyme prothrombin that circulates in the blood
so that it is changed into the enzyme thrombin.
Thrombin causes the plasma protein fibrinogen
to polymerize fibers of fibrin. The steps in the
sealing process are illustrated in
Figure 13.8
.
The clotting process is very complex, and from
a biomimetic point of view, it would be attractive
if a similar effect could be achieved with simpler
13.6 SELF-SEALING
Both animals and plants have mechanisms
that heal wounds rapidly so that only limited
amounts of liquid are lost. First the body makes
sure to close and seal the wound, and thereaf-
ter the healing takes place. Repairing damage
in blood vessels involves three steps: (1) form-
ing a plug in the hole (called
primary
hemostasis
),