Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
systemic biological response is among the most
important fundamental research problems in
biomaterials surface science
[16]
. Whatever the
mechanism, altering biomaterial hydrophilicity
works like magic in many applications.
The hydrophilic/hydrophobic terminology
used to describe water wetting has caused con-
siderable confusion in biomaterials because
these are relative terms with no universally
accepted reference scale
[19, 39]
. A sharp bifur-
cation in biomaterial surface properties near a
water wettability characterized by a 65° contact
angle serves as a convenient dividing line that
distinguishes hydrophilic from hydrophobic for
biomaterials applications, as mentioned in Sec-
tion
8.2.3.2
.
8.3.1.1 Reactive Gas-Discharge Surface
Treatment
Soon after Rappaport's pioneering studies of
mammalian cell adhesion
[40-42]
using chemical
methods to vary surface chemistry, a variety
of surface synthesis strategies were explored,
ranging from use of liquid-phase chemical
oxidants
[43, 44]
to the application of gas-
discharge surface treatments
[45]
. These latter
developments set the precedent for widespread
application of modern gas-discharge (plasma)
technology
[46, 47]
in biomedicine
[48, 49]
and
biotechnology
[50, 51]
. Various kinds of gas-
discharge technologies coarsely categorized in
Figure 8.5
have become an essential tool in sur-
face modification of biomaterials. For example,
sterile-disposable polystyrene tissue-culture
dishes and flasks, shown in
Figure 8.1
, are almost
universally oxidized using oxygen plasma
technology at high manufacturing speeds
[20]
.
Certain kinds of soft contact lenses are treated
similarly to prevent lenses from sticking to
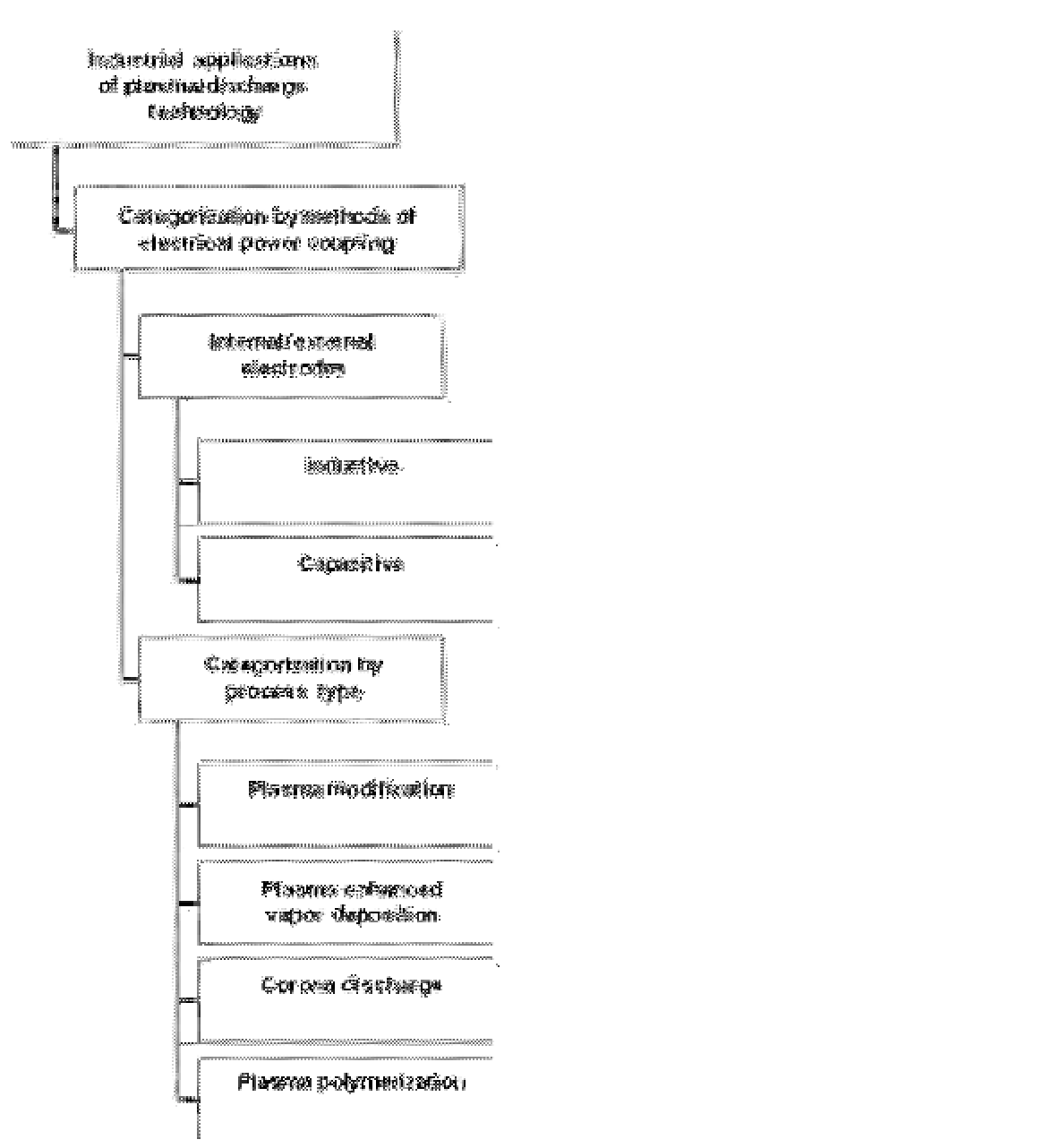
FIGURE 8.5
A coarse categorization of industrial applications of plasma/discharge technology in biomaterials modi-
fication. Two levels of organization, categories of electrical power coupling and process type, are shown. Internal and
external electrodes can be used in both inductive and capacitively coupled modalities. Among the discharge types,
plasma modification and corona discharge are widely used to affect biomaterial wettability. Plasma-enhanced vapor
deposition and plasma polymerization are related methods that deposit smooth, conformal coatings on biomaterial
surfaces.