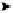Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
network system. The receiving exterior router removes the foreign header information and sends the
packets out the appropriate interface. Packets are encapsulated in User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
headers in the initial implementation of AURP.
When only two exterior routers are connected to a tunnel, that tunnel is called a
point-to-point tunnel
.
When more than two exterior routers are connected to the tunnel, that tunnel is called a
multipoint tunnel
.
If all exterior routers connected to a multipoint tunnel can send packets to each other, the tunnel is said
to be
fully connected
. If one or more exterior routers are not aware of other exterior routers, the tunnel
is said to be
partially connected
. Each exterior router functions both as an AppleTalk router within its
local internetwork and as an end node in the foreign network that connects the AppleTalk internetworks.
The main function of AURP is to maintain accurate routing tables for the entire AppleTalk WAN by the
exchange of routing information between exterior routers. In addition, AURP encapsulates AppleTalk
data packets with the headers required by the foreign network.
AURP uses the principle of split horizons (which states that it is never useful to send information about
a route back in the direction from which the information came) to limit the propagation of routing
updates. For that reason, an exterior router sends routing information about only the networks that
comprise its local internetwork to other exterior routers connected to the tunnel.
When an exterior router becomes aware of another exterior router on the tunnel, the two exterior routers
exchange their lists of network numbers and associated zone information. Thereafter, an exterior router
sends routing information only when the following events occur:
•
A network is added to the routing table.
•
A change in the path to a network causes the exterior router to access that network through its local
internetwork rather than through the tunnel or to access that network through the tunnel rather than
through the local internetwork.
•
A network is removed from the routing table.
•
The distance to a network is changed.
When an exterior router receives AppleTalk data packets or routing information that needs to be
forwarded over the tunnel, the AURP module converts that information to AURP packets. The AURP
packets are encapsulated in the header information required by the foreign network and sent over the
tunnel to the destination exterior router, as shown in Figure 9-7.
Figure9-7
The AURP Architectural Model
To tunnel
AURP packets
AURP module
Routing information
To local internetwork
To local internetwork
Routing information
Central routing
process
Routing information
At the destination exterior router, the AURP module removes the headers required by the foreign system
from the AURP packets and sends AppleTalk data packets to their final destination. The exterior router
uses the AURP packets that contain routing information to update its routing information tables but does
not propagate that information to any other exterior router.