Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Step 12.
Calculate the density of brine with dissolved methane.
First, calculate the specific volume of methane-free brine,
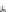
v
b
,0
, from
the density of methane-free brine,
ρ
b,0
, from equation (4.12).
(4.23)
Next, calculate the density of the brine with dissolved methane, in g/
cm
3
, from equation (4.24).
(4.24)
,
where
M
NaCl
is the molecular weight of sodium chloride (58.4428
g/g-mol), and
M
CH
4
is the molecular weight of methane (16.043 g/g-mol).
If desired, the specific volume of brine with dissolved methane, in
cm
3
/g, may be obtained from the reciprocal of the density, as shown in
equation (4.25).
(4.25)
Compressibility of brine containing dissolved methane
The equation for compressibility of brine with dissolved methane
is obtained from the definition of the coefficient of isothermal
compressibility and the equation for specific volume of brine with
dissolved methane, equation (4.25).
The coefficient of isothermal compressibility may be defined as the
fractional change in specific volume per unit change in pressure, i.e.,
equation (4.26).
(4.26)
In combining equations (4.25) and (4.26), there are two cases to
consider. The simpler case is for a single-phase brine system. In this












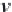


















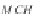



































































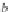

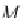

































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search