Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
condensate at the surface, the specific gravity and compositions of
the nonhydrocarbons of the surface gas can be used to represent the
reservoir gas. If there is petroleum condensate with the gas at the surface,
a recombination calculation given by Gold et al. can be used to calculate
the specific gravity of the reservoir gas.
1
If the reservoir pressure is less
than the dew point pressure of the reservoir gas, the Gold et al. procedure
will give an estimate of the specific gravity of the reservoir gas but will
not represent the total (gas plus condensate) fluid in the reservoir.
Values of compositions of nonhydrocarbons measured with the surface
gas can be used as reasonable estimates of these compositions for the
reservoir gas.
The best available gas z-factor correlation equations/procedure is very
accurate; the results are as accurate as normally reported in petroleum
industry fluid property studies (PVT reports). The various properties
calculated using these z-factors are also of good accuracy. The best
available gas viscosity correlation does not have the precision of the best
z-factor correlation but does give results of sufficient accuracy for use in
petroleum engineering calculations.
Gas z-Factors
Gas z-factors are also called
gas compressibility factors
or
gas deviation
factors
. Gas z-factors are defined as
(2.1)
and are used to adjust the ideal gas equation to calculate real gas
volumes.
(2.2)
Standing and Katz proposed a graphical correlation of gas
z-factors plotted against pseudoreduced pressures and pseudoreduced
temperatures.
2
These pseudoreduced properties are defined as
(2.3)


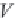











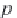
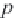





































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search