Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Oil formation volume factors at reservoir pressure equal
to bubblepoint pressure
McCain derived an equation for calculating oil formation volume
factors at bubblepoint pressures.
38
This equation, equation (3.21a),
is recommended for estimating oil formation volume factors at
bubblepoint pressure.
(3.21a)
This is not a correlation; rather it is the result of a material balance
equating the mass of oil leaving the reservoir to the mass of the
stock-tank oil plus the mass of the total surface gas. The advantage of
its use is that values of oil formation volume factors, oil densities, and
solution gas-oil ratios will be consistent with each other.
In application, correlation equations must be used to determine
values of the bubblepoint pressure,
p
b
, and values of the density of the
reservoir oil at that bubblepoint pressure,
ρ
oRb
. Equations (3.7) and
(3.18a)-(3.18h) are recommended.
Note that the value of the gas specific gravity in equation (3.21a)
should be the weighted-average specific gravity of the total surface gas.
Thus, either equation (3.4) or equation (3.6) is usually necessary with
equations (3.5) and (3.2) used to obtain the stock-tank gas properties.
Evaluation of proposed correlation equations for oil formation
volume factors at bubblepoint pressure
The 718 reservoir fluid studies in the data set described in table 3-9
each had a separator test from which a value of oil formation volume
factor at the bubblepoint was obtained. These values were used to
evaluate published correlation equations of oil formation volume
factors at bubblepoint pressures. The evaluation is given in table 3-19.



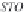



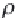


































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search