Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
0.06
wBruCon
wBruOri
wBruAus
Total
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
0
Fat body
Malpighian tubule
Gut
Testis
Nurse tissue
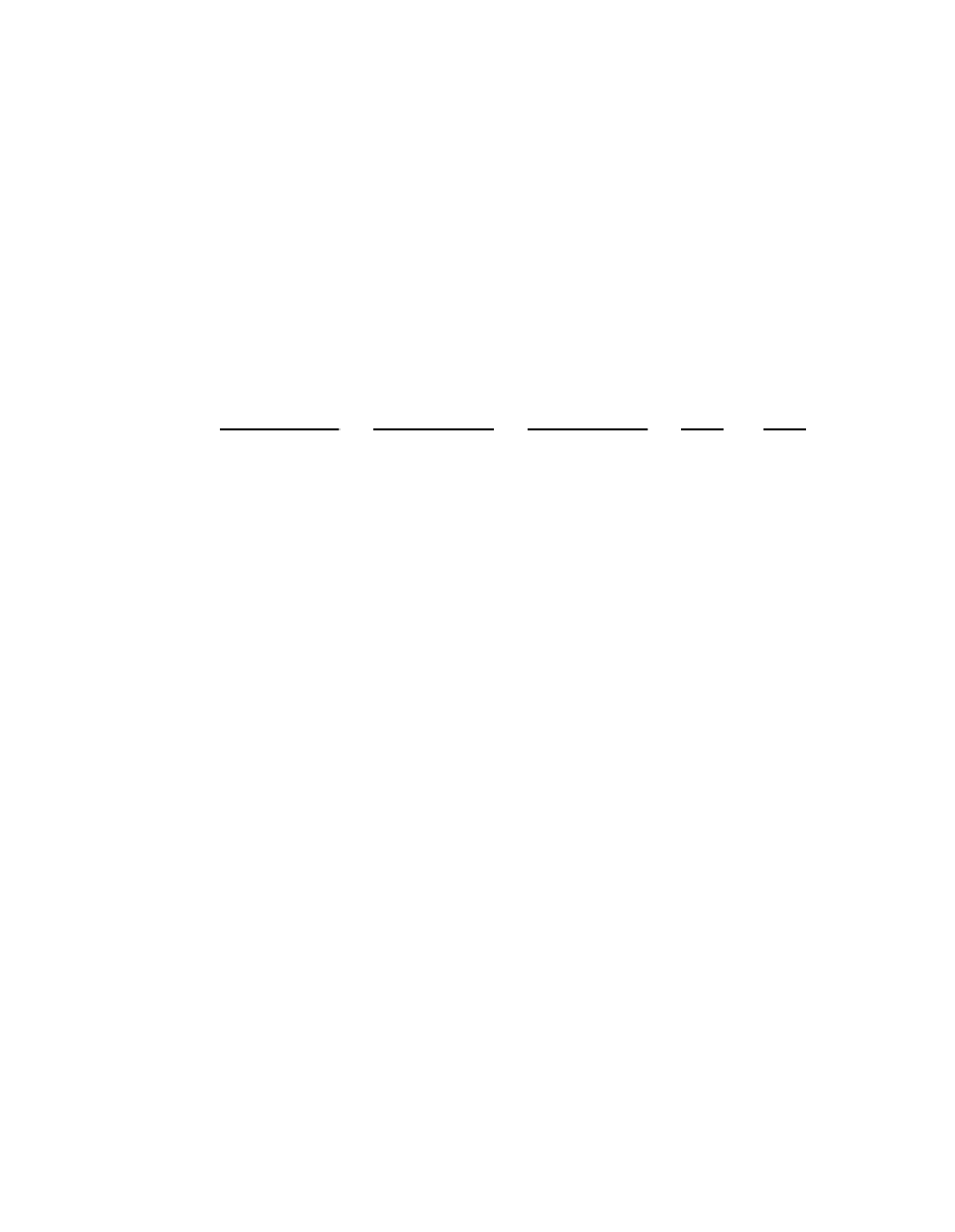
FIGURE 18.7
Infection density of wBruCon, wBruOri, and wBruAus in different tissues and organs of
C.
chinensis
in terms of
wsp
copies per COII copies. The mean and standard deviation for Ýve samples are shown
for each tissue or organ. Newly emerged adults were subjected to the analysis. [From Ijichi, N., Kondo, N.,
Matsumoto, R., Shimada, M., Ishikawa, H., and Fukatsu, T. (2002).
Appl. Environ. Microbiol.
68:
4074Ï4080.
With permission.]
was standardized by copy number of a host gene, mitochondrial COII. It was demonstrated that
both the density and the composition of the three
Wolbachia
strains were speciÝc to tissues and
organs of
C. chinensis
.
Total densities of the three
Wolbachia
strains exhibited signiÝcant differences between tissues
and organs (Figure 18.7). Among the tissues and organs examined, for example, higher levels of
Wolbachia
infection were detected in the nurse tissue and fat body than in the gut and testis. The
total densities of the
Wolbachia
also showed sex-related differences. For example, in fat body the
density of
Wolbachia
was higher in females than in males, while in Malpighian tubules the density
of
Wolbachia
was lower in females than in males.
The compositions of the three
Wolbachia
strains also showed signiÝcant differences between
tissues and organs
(Figure 18.8).
In fat body, wBruCon accounted for around 80% of the total
Wolbachia
population, wBruOri about 15 to 18%, and wBruAus a small fraction. In gut and testis,
wBruCon comprised about 50 to 70% of the total
Wolbachia
population, wBruOri around 30 to
40%, and wBruAus around 10% or less. In Malpighian tubule, a sex-related difference was detected;
in males, wBruOri was the predominant strain, whereas in females wBruCon was the major
component. Strikingly, in nurse tissue and oocyte, wBruOri accounted for more than 80% of the
total
Wolbachia
population, whereas wBruCon and wBruAus constituted only small fractions.
DIFFERENTIAL TISSUE TROPISM OF THE THREE
WOLBACHIA
STRAINS IN THE SAME HOST INSECT
Based on these results,
it was demonstrated that interesting patterns of differential tissue tropism and
population dynamics of wBruCon, wBruOri, and wBruAus existed in the same host insect throughout
the developmental course. Although very poorly understood at present, the different patterns in tissue
localization and proliferation of the three
Wolbachia
strains must reÞect various biological aspects of
hostÏsymbiont and symbiontÏsymbiont interactions. The mechanisms controlling the tissue tropism