Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Mechanisms of ProkaryoteÏEukaryote Horizontal Gene Transfer:
Horizontal Genome Transfer from
Wolbachia
Endosymbiont to X Chromosome
of
C. chinensis
................................................................................................................................319
Inactivated
Genes on Host Chromosome ....................................................................319
Wolbachia
ENDOSYMBIOTIC BACTERIA OF THE GENUS
WOLBACHIA
Members of the genus
Wolbachia
constitute a group of rickettsia-like endocellular bacteria in the
b
is universally found in insects and
less frequently in mites, spiders, crustaceans, and nematodes.
subdivision of the proteobacteria. Infection with
Wolbachia
endosymbionts have
attracted a great deal of attention from biologists because they often cause a wide range of effects
on the reproduction and physiology of arthropod hosts such as cytoplasmic incompatibility (CI),
parthenogenesis, feminization, male killing, and others. Because
Wolbachia
are inherited solely
through the maternal lineage of the host by vertical transmission, these reproductive phenotypes
are regarded as the selÝsh strategies whereby
Wolbachia
increase the frequency of infected females
in host populations often at the expense of the host Ýtness (OÔNeill et al., 1997; Werren, 1997;
Stouthamer et al., 1999).
Wolbachia
THE ADZUKI BEAN BEETLE,
CALLOSOBRUCHUS CHINENSIS
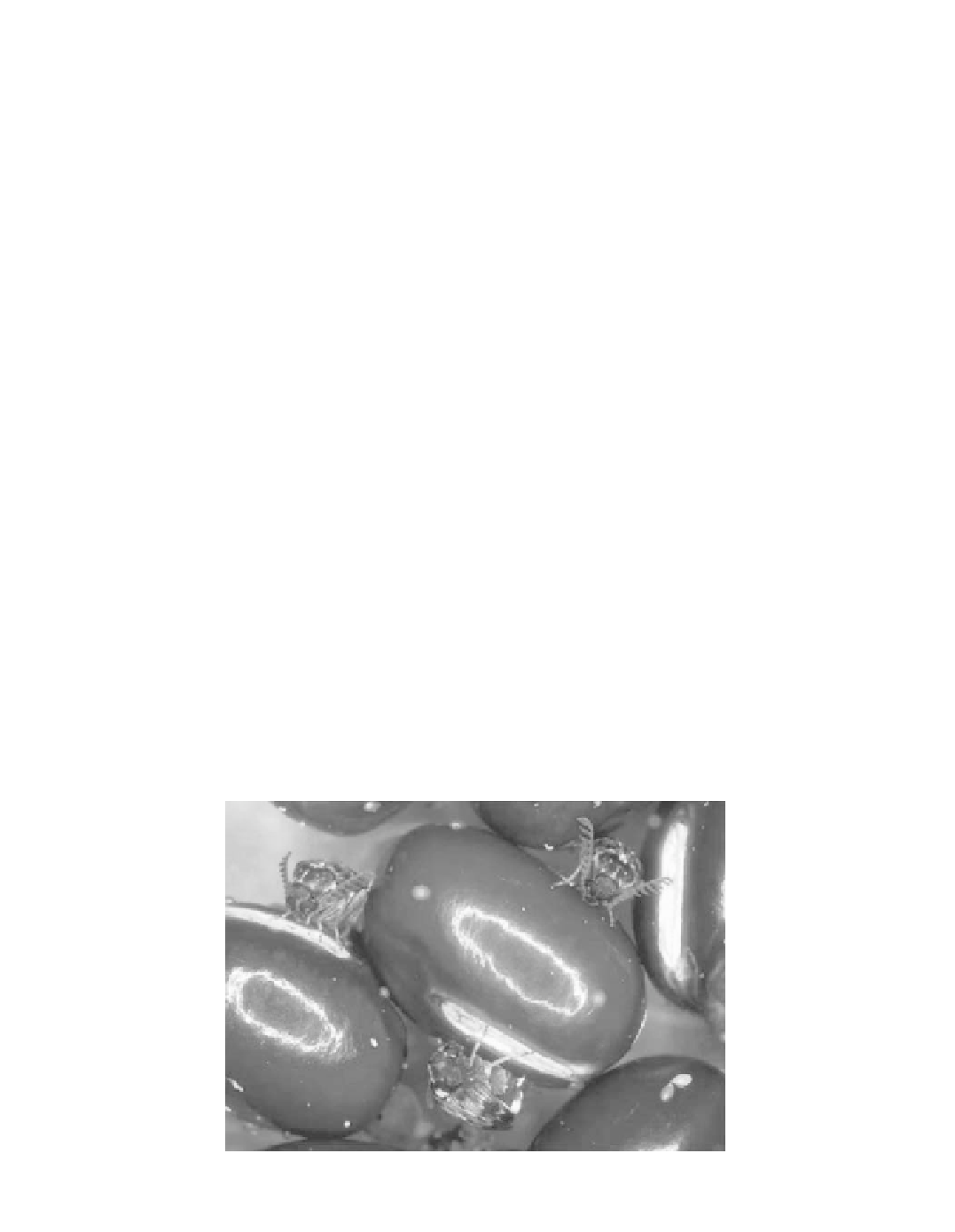
Callosobruchus chinensis
(Coleoptera: Bruchidae) is known for infesting stored beans such as
Vigna
spp. (Figure 18.1). In addition to its importance as a pest insect, the beetle has been widely
FIGURE 18.1
Female adults of
Callosobruchus chinensis
ovipositing on adzuki beans
Vigna angularis
.