Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
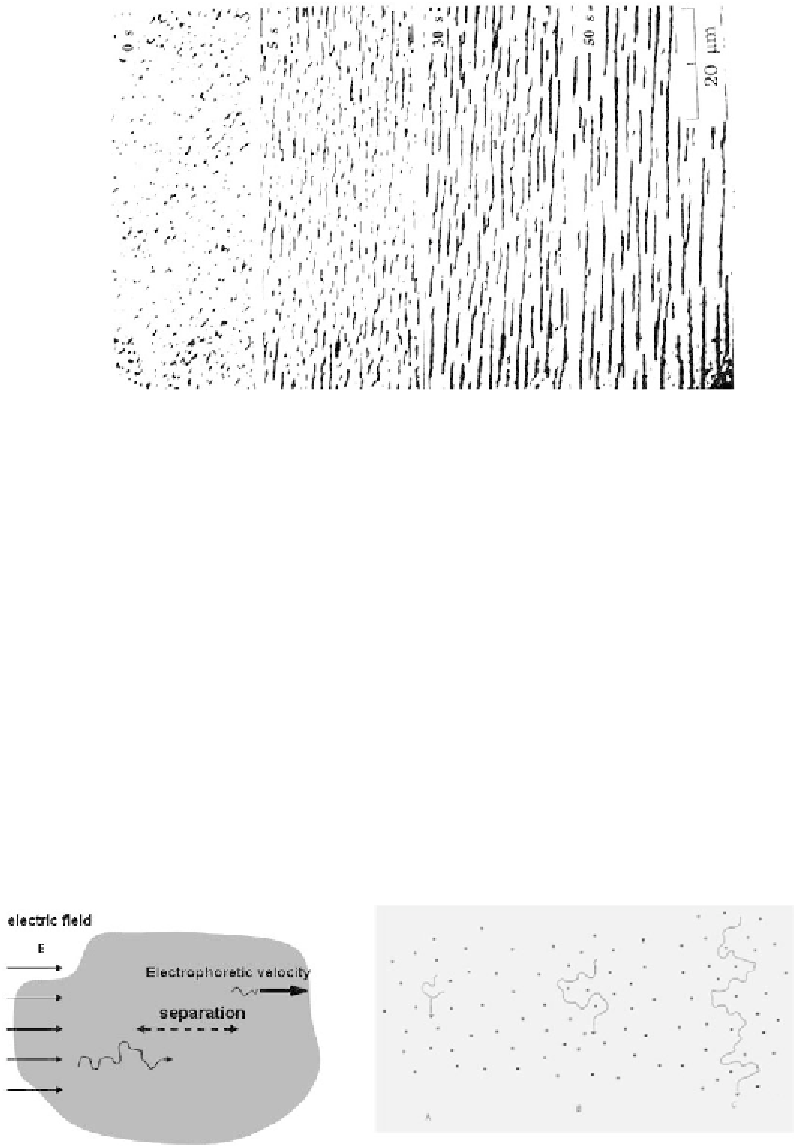
Figure 9.31
Chains of magnetic beads, aligned with the applied magnetic field, form in less than
1 minute.
the order of 24 hours. Some other solutions have been searched to obtain shorter
separation times. The idea was to mimic the action of a gel by using lithography
techniques to fabricate a lattice of micropillars. Due to the difficulty in fabricating
this type of microcomponent, an interesting solution with magnetic beads has been
set up [24, 25]. Magnetic beads (2.8
μ
m Dynal) initially dispersed in a flat micro-
channel limited between two plates form vertical columns (vertical chains) when
an external magnetic field is applied vertically. The columns are naturally regularly
spaced and they perform the same function as gels during DNA electrophoresis.
However, the separation duration is much shorter than that of gels (100 mn instead
of 24 hours). In this case, magnetic beads assembly is similar to a “calibrated” gel
(Figure 9.33).
Figure 9.32
Left: schematic view of DNA fragments of different sizes migrate at different speed in
an agarose gel under a constant electric field. Right: a longer strand encounters more difficulties to
move in the porosities of the gel than a shorter one.