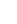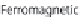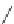Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
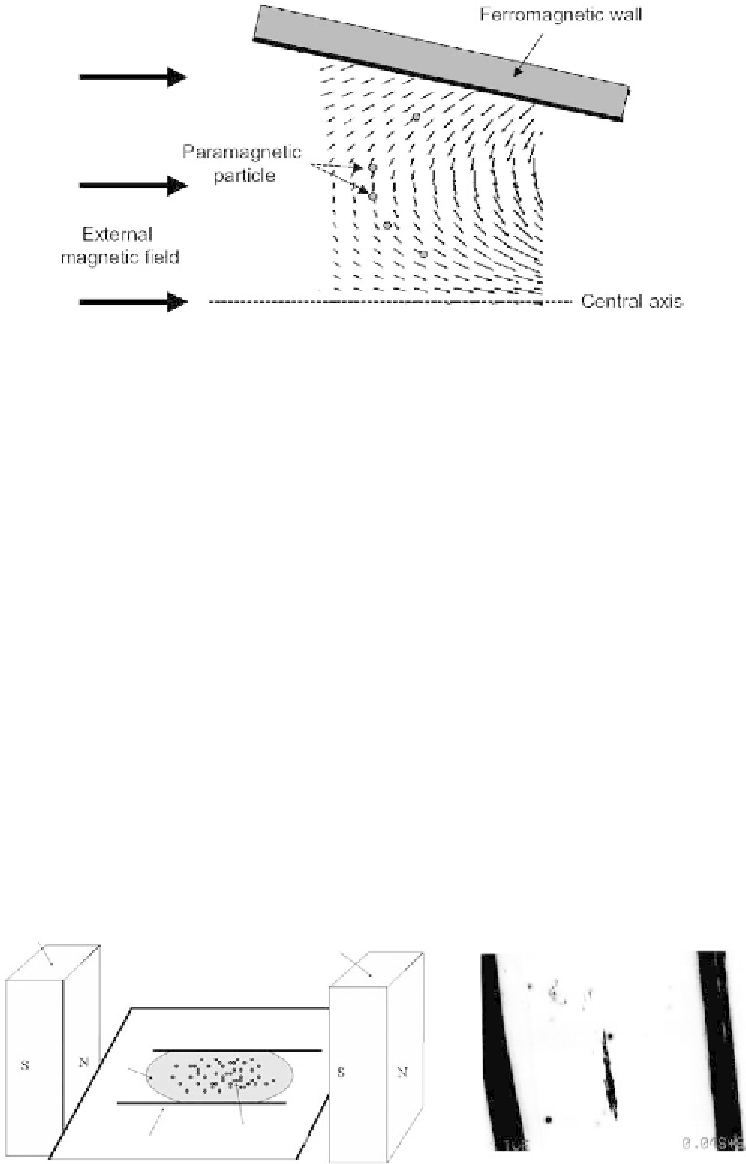
Figure 9.15
Force field created by two oblique symmetric ferromagnetic plates in a uniform
external magnetic field. (
From
[15].)
9.6 Magnetic Repulsion
In the previous section, it has been observed that the magnetic force field in the
vicinity of a cylindrical rod placed in a uniform external magnetic field is highly
nonuniform. The force is directed towards the rod in the regions aligned with the
external field (from the rod center) and directed away from the rod in the regions
perpendicular to the external field (from rod center). This observation can be ex-
tended to any shape of ferromagnetic body. We can even imagine more than one
body in the external field as shown in Figure 9.14 and obtain a confinement zone
for the magnetic particles in a region located between the ferromagnetic bodies.
Note that the particles are not completely at rest in the confinement zone: they are
repelled from the walls, and they move along the central axis to exit on both sides,
as shown in Figure 9.15 from the calculation of the magnetic force field.
Figure 9.15 Force field created by two oblique symmetric ferromagnetic plates
in a uniform external magnetic field. (From [15].)
A very simple experimental setup may be realized to illustrate the principle of
magnetic repulsion [15] (Figure 9.16). Place two ferromagnetic wires on a glass
Figure 9.16
Experimental verification of the magnetic repulsion principle. Paramagnetic
microparticles (1
μ
m) repulsed from two ferromagnetic parallel wires.