Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
principle of magnetic separators: we shall see that there are magnetic attraction
zones and repulsion zones around the rod and particles are expelled from the
repulsion zones towards the attraction zones and concentrate on some regions on
the rod surface. Assembly of ferromagnetic rods located in a large external mag-
netic field are called high gradient magnetic separators (HGMSs) and are widely
used in chemical and biological processes to remove magnetic particles from a
carrier fluid [12].
9.5.1 Governing Equations
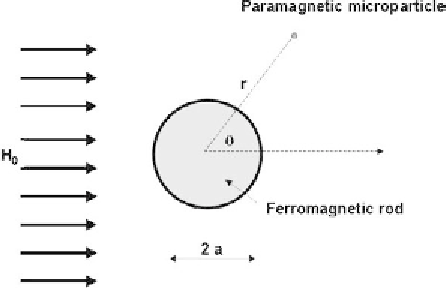
Suppose a ferromagnetic rod of radius
a
, surrounded by a carrier fluid containing
paramagnetic microparticles and placed in a uniform external magnetic field
�
H
0
(Figure 9.9).
In this problem, there is no electric current and the use of the magnetic scalar
potential
f
is sufficient to solve the problem. Using the relation
�
H
= -
grad
φ
( )
the potential
f
is then the solution of the following equation
®
�
div
(
-
µ µ
grad
( ))
φ
+
div M
(
µ
) 0
=
(9.19)
0
r
0
r
where
μ
r
is the relative magnetic permeability of the different materials of the com-
putational domain. The remanent magnetization may be supposed uniform in the
rod, then (9.19) reduces to
®
div
(
-
µ µ
grad
( )) 0
φ
=
(9.20)
0
r
Equation (9.20) might not be linear if the external magnetic field is large enough to
saturate parts of the ferromagnetic regions. Note that
f
is continuous on the whole
computational domain even at the boundaries between different materials. The
Figure 9.9
Schematic view of a ferromagnetic rod in an external magnetic field.