Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 7.31
Sketch of the homogeneous reaction in flowing solution.
and, if we use the notations
c
c
D
c
A
,0
*
A
*
B
A
c
=
,
c
=
,
χ
=
,
β
=
A
B
c
c
D
c
A
,0
B
,0
B
B
,0
the system (7.60) becomes
*
2 *
¶
c
¶
c
1
A
A
*
*
=
χ
-
c
c
A
B
*
*2
β
¶
x
¶
y
(7.62)
*
2 *
¶
c
1
¶
c
B
B
*
*
=
-
β
c
c
A
B
*
χ
*2
¶
x
¶
y
This system is nondimensional and depends only on the two parameters
c
and
b
. Again, this system is nonlinear, and strongly coupled. The use of numerical meth-
ods is required to solve such systems. In Figure 7.32, we show the computed solu-
tion obtained with the numerical software COMSOL.
7.4.2 Heterogeneous Reactions
Biochemical reactions are said heterogeneous when a ligand is immobilized on
the solid walls and the targets (also called analytes or reactants) are in solution.
Heterogeneous reactions are widely used in microsystems [16]. They appear to
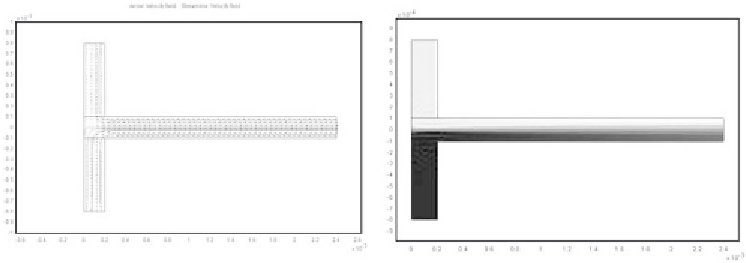
Figure 7.32
View of the flow velocities (left) and the reaction zones (right) in the T shape channel.
Calculation performed with the FEMLAB numerical software.