Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where
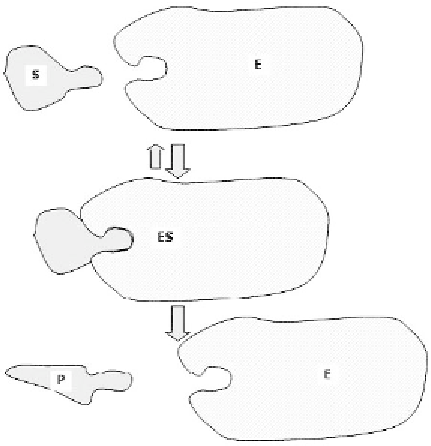
E, S,
and
P
refer respectively to enzyme, substrate, and product concentra-
tion. Note that the name “substrate” corresponds to the species that is undergoing
the chemical reaction. The notation
ES
refers to an intermediate state where the
substrate
E
is bonded to the enzyme
E
(Figure 7.15).
If we note
k
1
,
k
-1
an
k
2
the rate constant of the 2 reactions of equation (7.19),
the kinetics of
ES
binding is given by
d ES
[
]
=
k E S
[
][ ]
-
k ES
[
]
-
k ES
[
]
(7.20)
1
2
-
1
d t
And the product concentration kinetics is
d P
[
]
V
=
=
k ES
[
]
(7.21)
2
d t
The Michaelis-Menten approach is based upon the simplification that assumes
that the rate of production of
ES
concentration is constant, i.e.
d ES
[
]
=
k E S
[
] [ ]
-
k ES
[
]
-
k ES
[
] 0
=
(7.22)
1
2
-
1
d t
Then, we have the relation
k
1
[
ES
]
=
[
E S
] [ ]
(7.23)
k
+
k
2
-
1
If we note that the total (initial) concentration of enzyme is
[
E
]
=
[
E
]
+
[
ES
]
(7.24)
0
Figure 7.15
Schematic view of the enzymatic reaction.