Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 7.2
(a) Double-helix DNA structure. (b) Hydrogen bonds between A and T (Adenine and
Thymine), and C and G (Cytosine and Guanine).
A similar lock and key approach can be done for antigen (or proteins) [2].
Roughly speaking, an antibody is a very complex molecule having a Y shape as
symbolized in Figure 7.4. An antibody can recognize a specific antigen approaching
one of the two binding sites located on both ends of the Y. The bond is made of
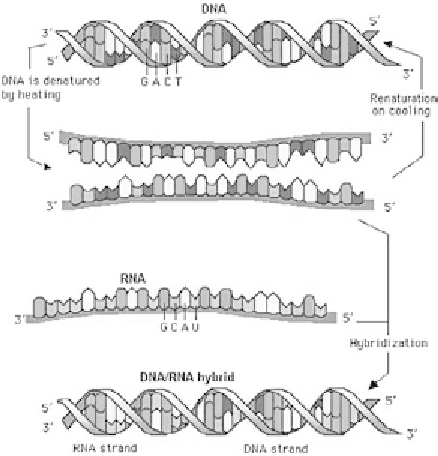
Figure 7.3
DNA denaturing and hybridization with a complementary sequence. (a) DNA double
strand, (b) denaturing, (c) RNA copy, (d) hybridization.