Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 1.9
The capillary length
l
for a large droplet corresponds to the curved part of the
droplet.
conductive droplet is submitted to an electric field, its deformation is linked to the
electrical Bond number defined as
2
ε
E R
Bo
=
e
γ
where
E
is the electric field and
e
the electrical permittivity of the liquid.
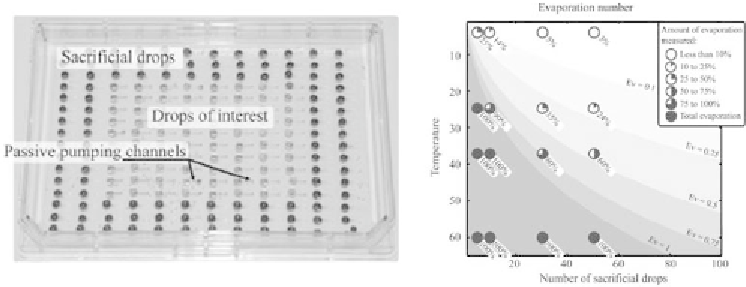
In biotechnology, when working with droplets, evaporation must be avoided
as much as possible [14]. Closed atmosphere and sacrificial droplets are often used
to maintain a constant vapor pressure and limit evaporation [Figure 1.10(a)]. The
evaporation number indicates whether the quantity of water contained in the sacri-
ficial droplets is sufficient to limit the evaporation from the droplets of interest [15].
More specifically, recalling that the evaporation rate of a microdrop is proportional
to its radius, the relative evaporation of droplets of interest compared to the total
relative evaporation is given by
å
å
R
E
i
i
å
R
ρ
V
D
ρ
V
V
i
i
sat
a
i
(1.21)
Ev
=
=
=
å
å
å
V
E
R
R
ρ
i
V
V
D
ρ
loss
sat
a
where
R
i
is the radius of the droplets of interest,
V
i
and
E
i
are the initial total vol-
ume of liquid of interest and its evaporation rate,
V
loss
is the liquid volume that is
Figure1.10
(a) The evaporation from droplets of interest is less than 0% when the evaporation
number is smaller than 0.. (b) Evaporation from sacriicial droplets maintains the water vapor pres-
sure in a closed box and prevents noticeable evaporation of droplets of interest. Reprinted with
permission from []. Copyright 00 Royal Society of Chemistry.